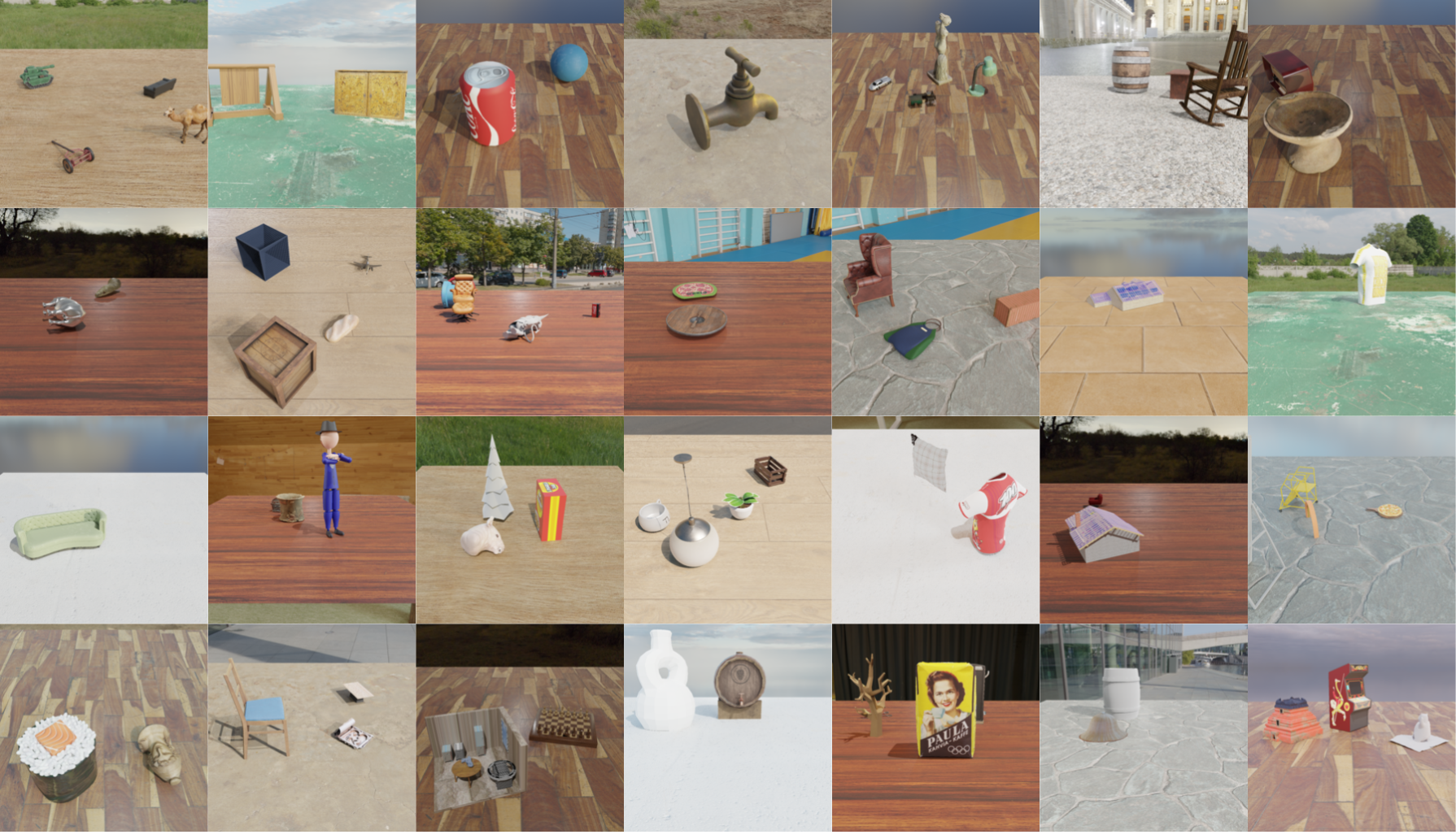

The task of 3D-aware image editing involves editing an image in a way that is consistent with some transformation to its underlying 3D scene. We present a model and dataset for this task and show impressive transfer to the real-world....
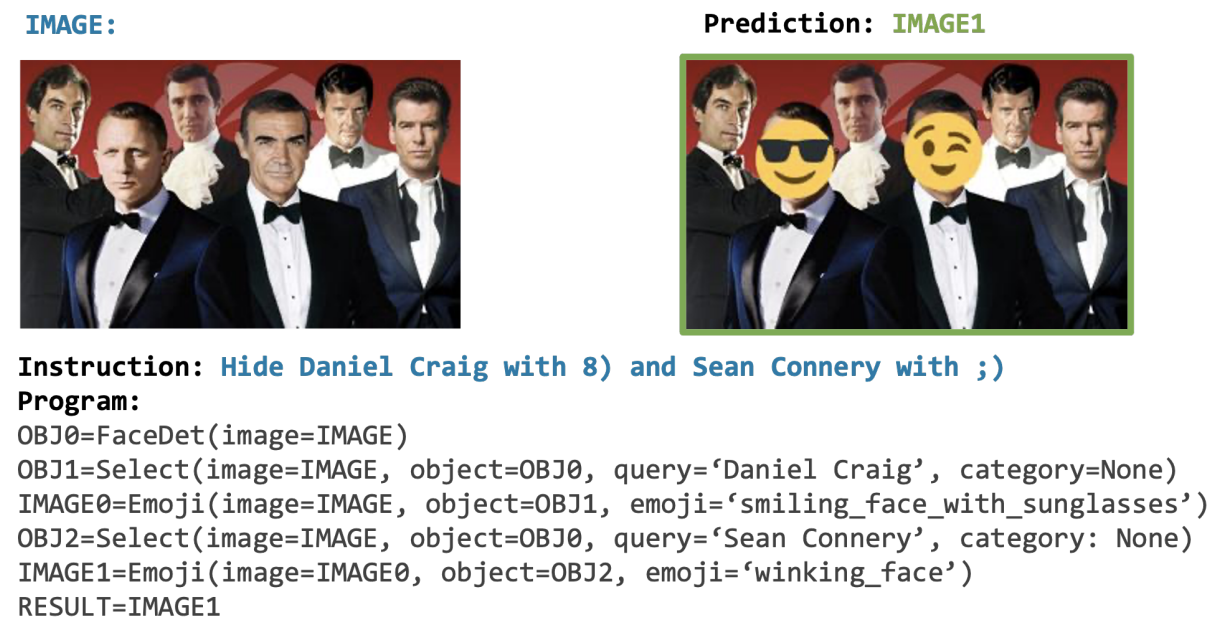
[CVPR 2023 Best Paper] VISPROG is a neuro-symbolic system for solving complex and compositional visual tasks by generating and executing programs.
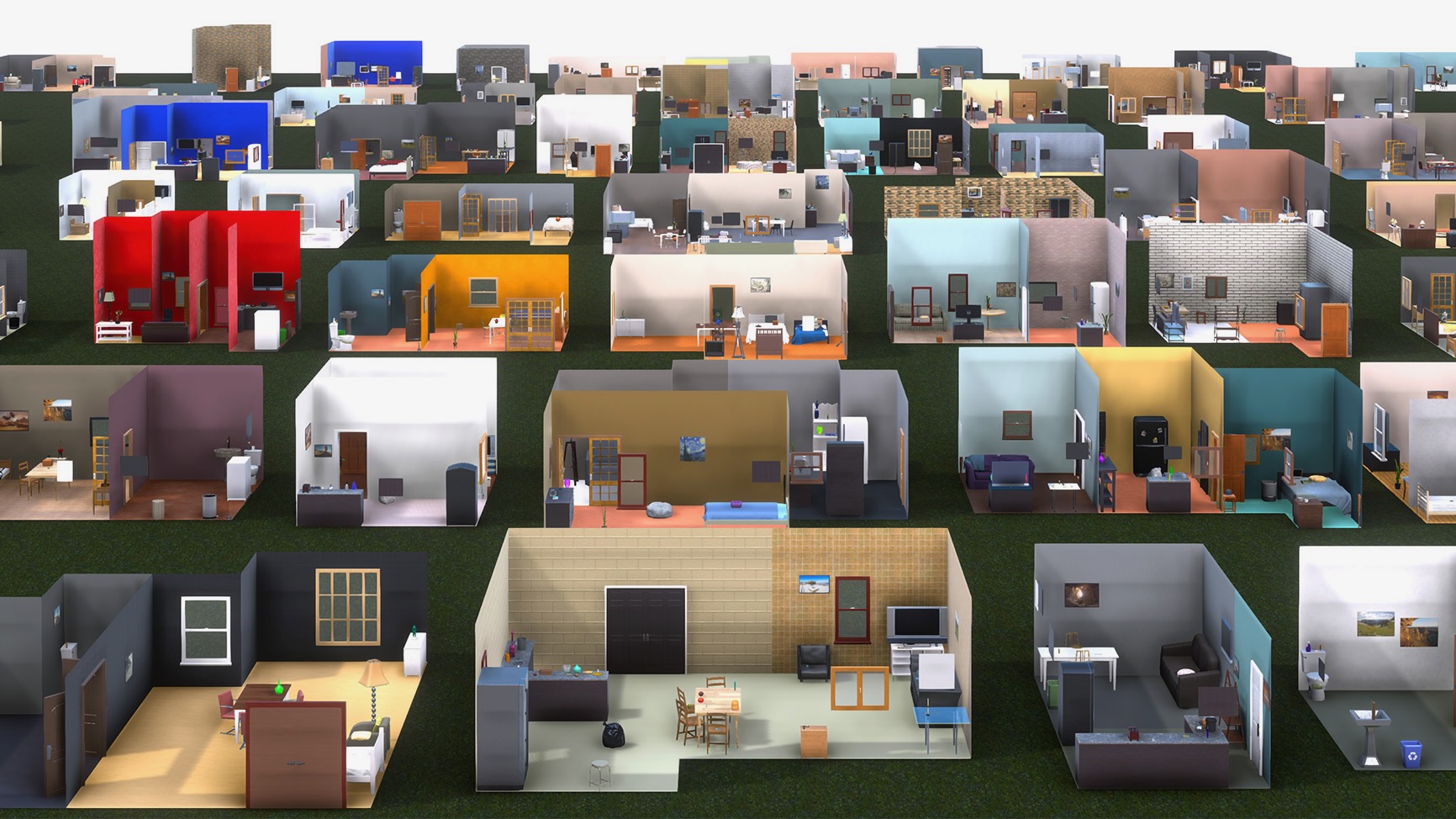

[Neurips 2022 Outstanding Paper] ProcTHOR is a platform to procedurally generate realistic, interactive, and diverse simulated 3D environments. It dramatically scales up the amount of training data which significantly improves performance on all embodied tasks considered.
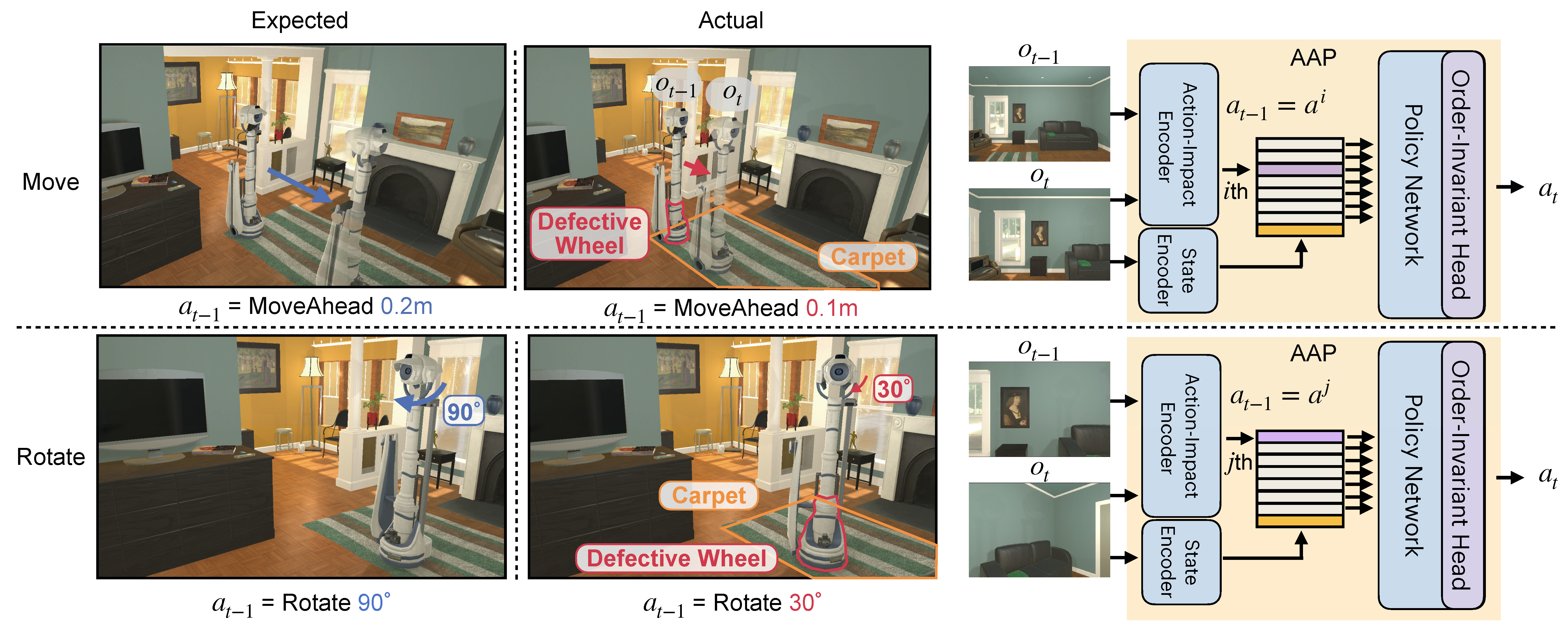
An embodied agent may encounter settings that dramatically alter the impact of actions: a move ahead action on a wet floor may send the agent twice as far as it expects and using the same action with a broken wheel...
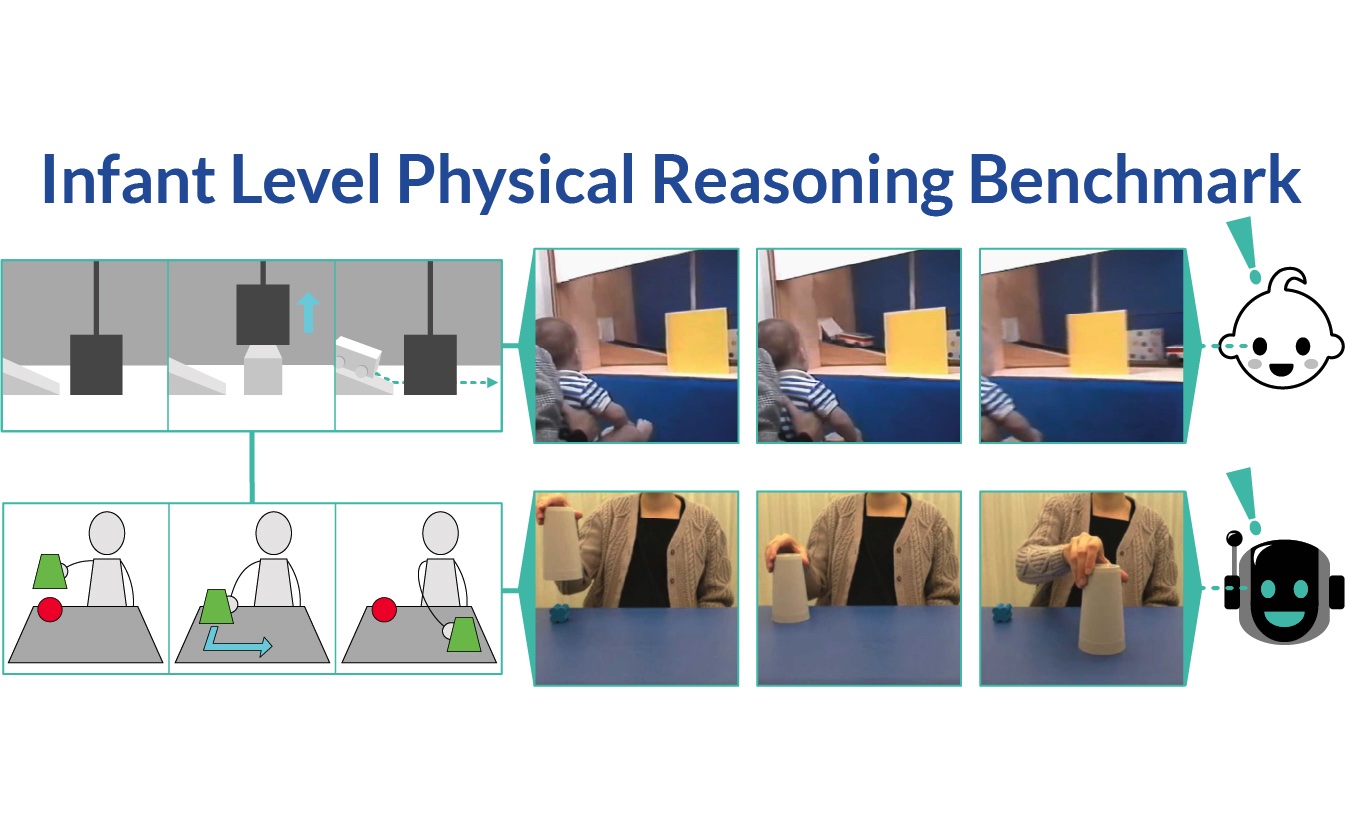
Inspired by research on infants, we introduce the Infant-Level Physical Reasoning Benchmark (InfLevel) to better understand the fundamental physical reasoning abilities of AI systems. We find that current popular systems appear to be far less proficient than infants.
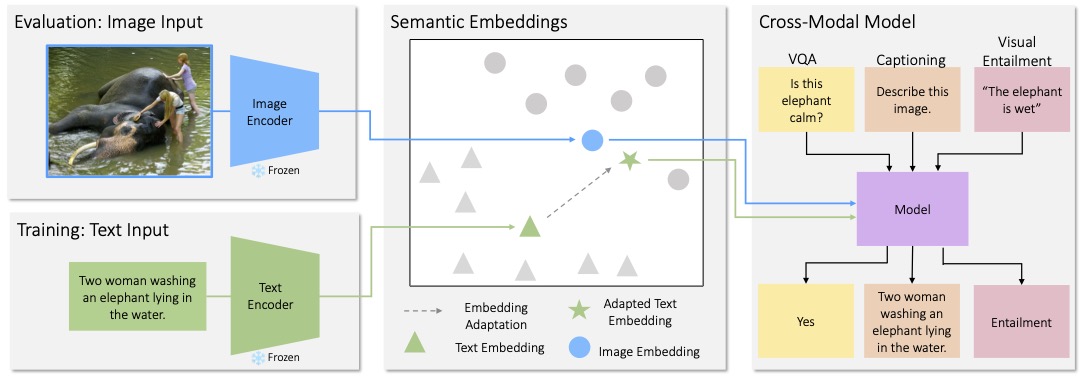
CLOSE is a cross-modal transfer model that learns skills from textual data and then use them to complete vision tasks without ever training on visual data. It works by exploiting the joint embedding space of contrastively trained vision and language...
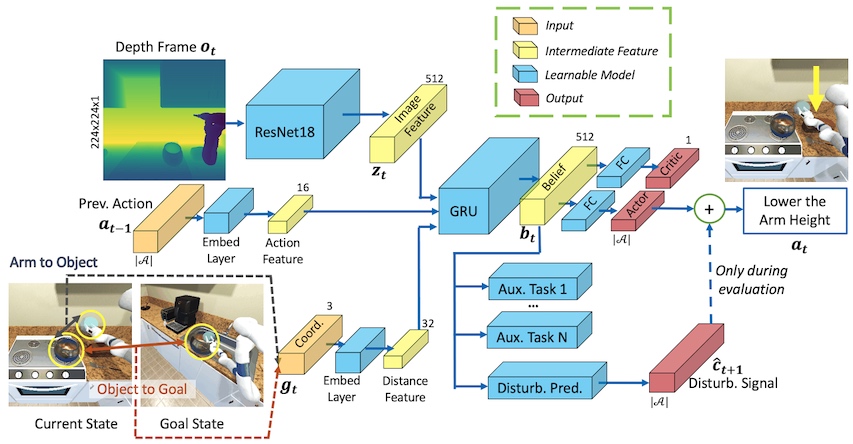
In this work, we take the first step towards collision/disturbance-free embodied AI agents for visual mobile manipulation, facilitating safe deployment in real robots.
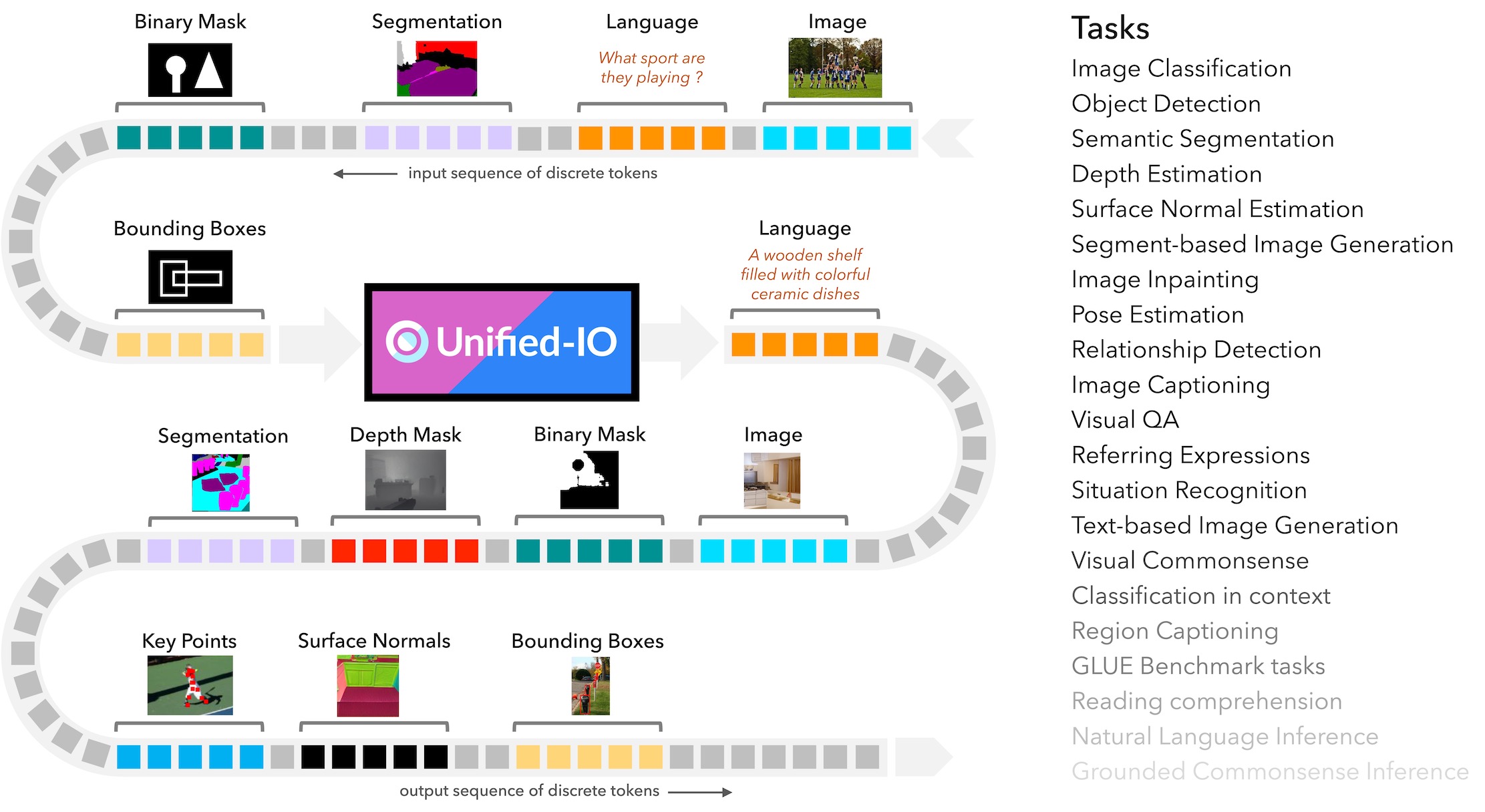
Unified-IO is the first neural model to perform a large and diverse set of AI tasks spanning classical computer vision, image synthesis, vision-and-language, and natural language processing.
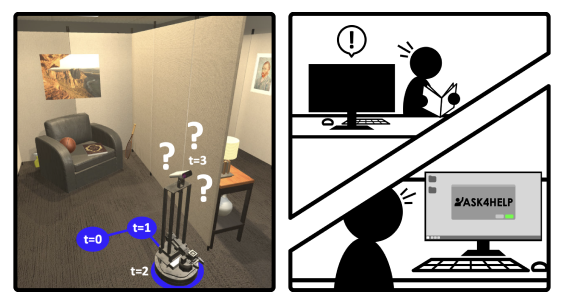
We propose Ask4Help, a policy that endow off-the-shelf embodied models with the ability to request expert assistance. We show that we can improve navigation and rearrangements with limited expert help.

A-OKVQA is a new knowledge-based visual question answering benchmark. It is an Augmented successor of the OK-VQA benchmark and contains a diverse set of 25K questions requiring a broad base of commonsense and world knowledge to answer.
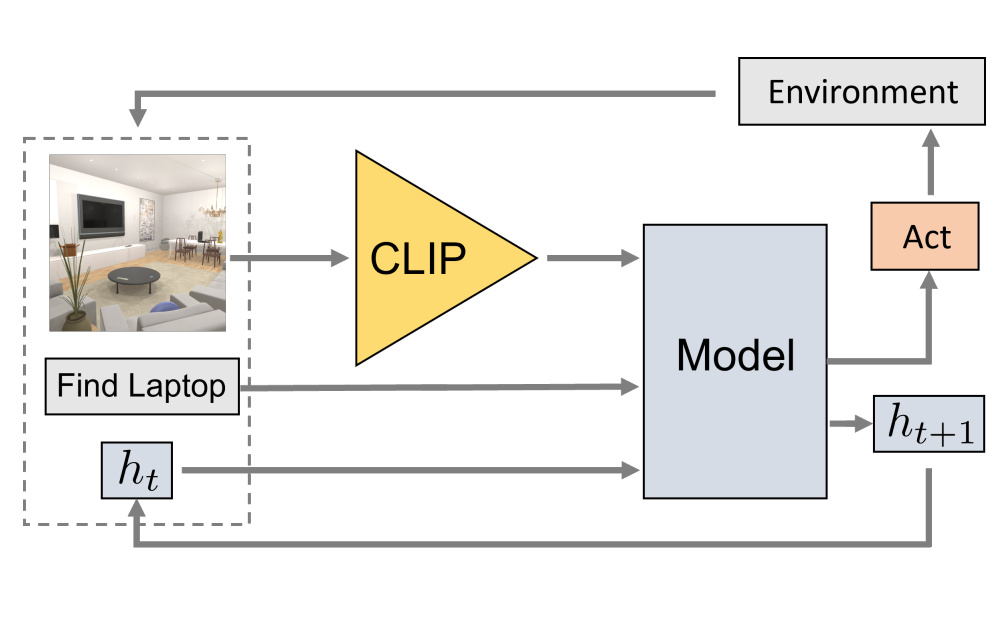
We present competitive performance on navigation-heavy tasks in Embodied AI using frozen visual representations from CLIP.

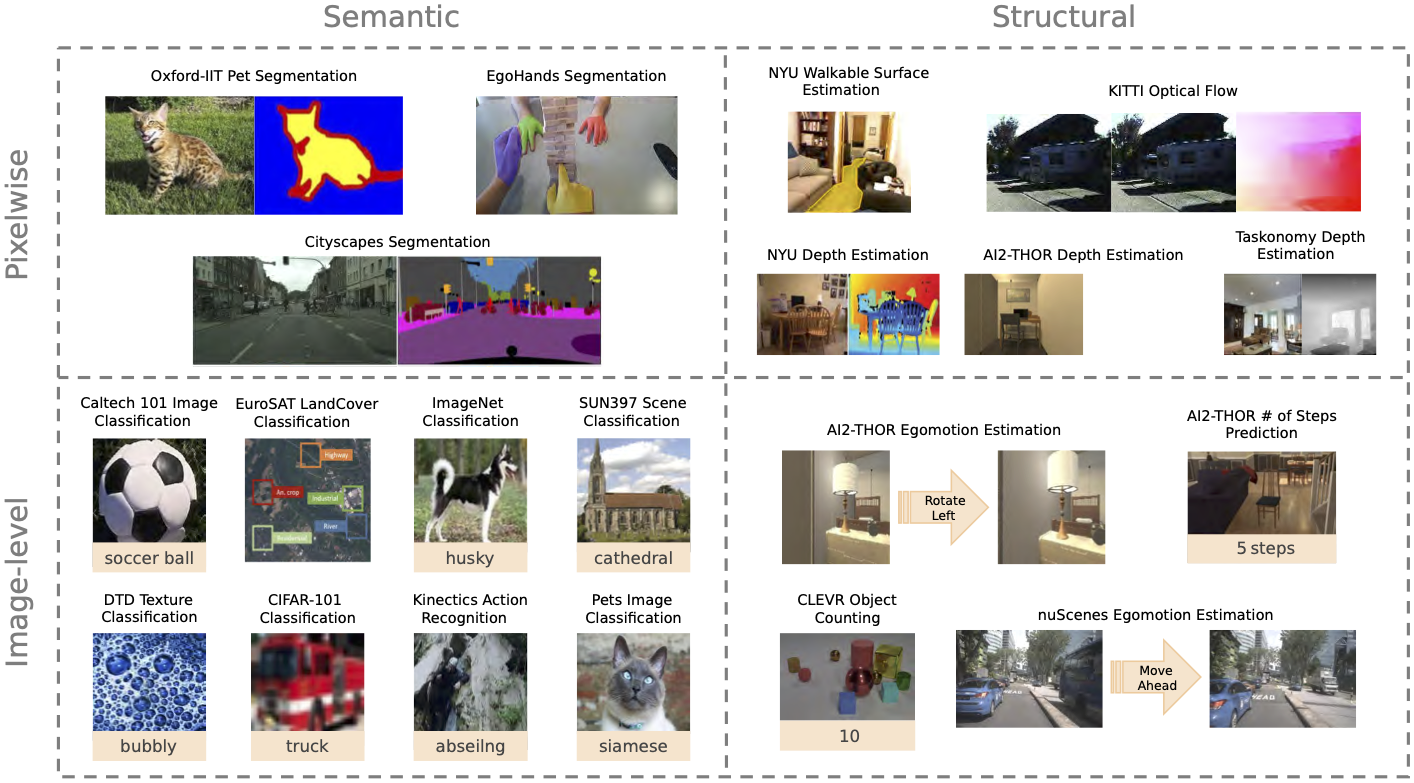
The General Robust Image Task (GRIT) Benchmark is an evaluation-only benchmark for evaluating the performance and robustness of vision systems across multiple image prediction tasks, concepts, and data sources.
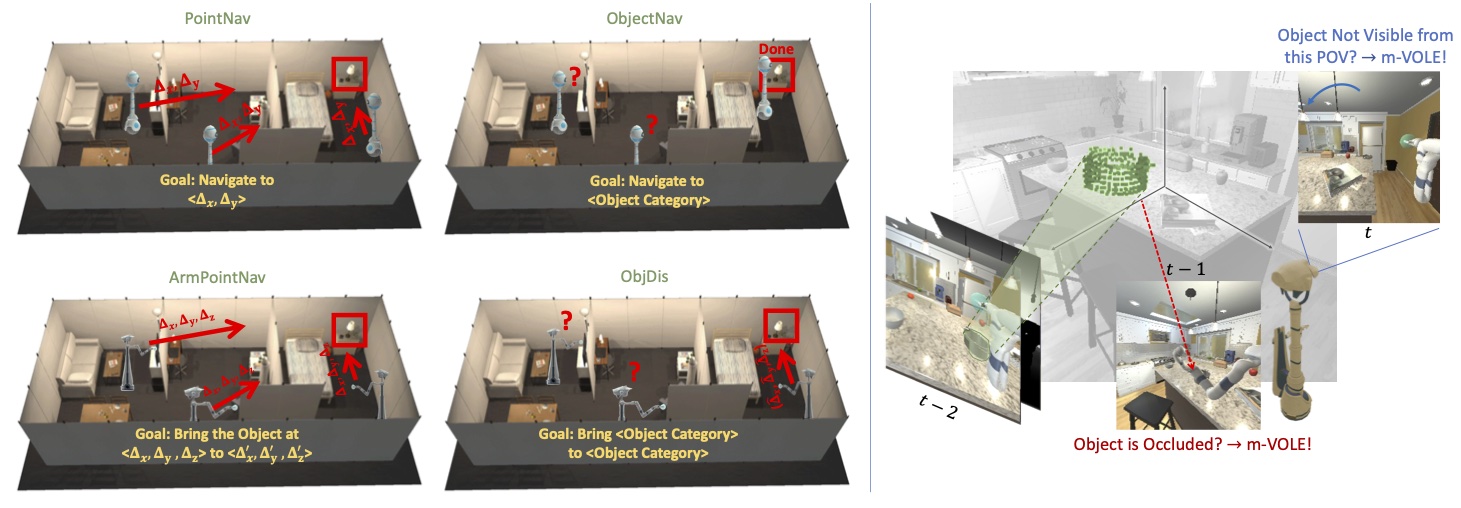
We propose Manipulation via Visual Object Location Estimation (m-VOLE), an approach that explores the environment in search for target objects, computes their 3D coordinates once they are located, and robustly aids the task of manipulating these objects throughout the episode....
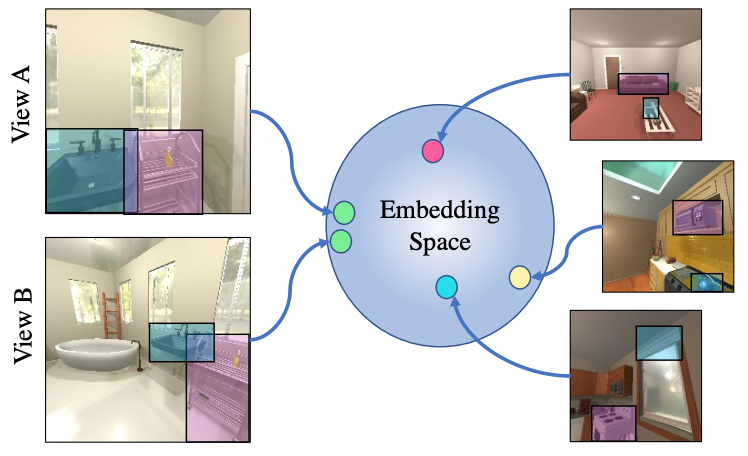
We employ a contrastive loss to embed relationships between objects as features and show how our representation can be used downstream for visual room rearrangement without any additional training.
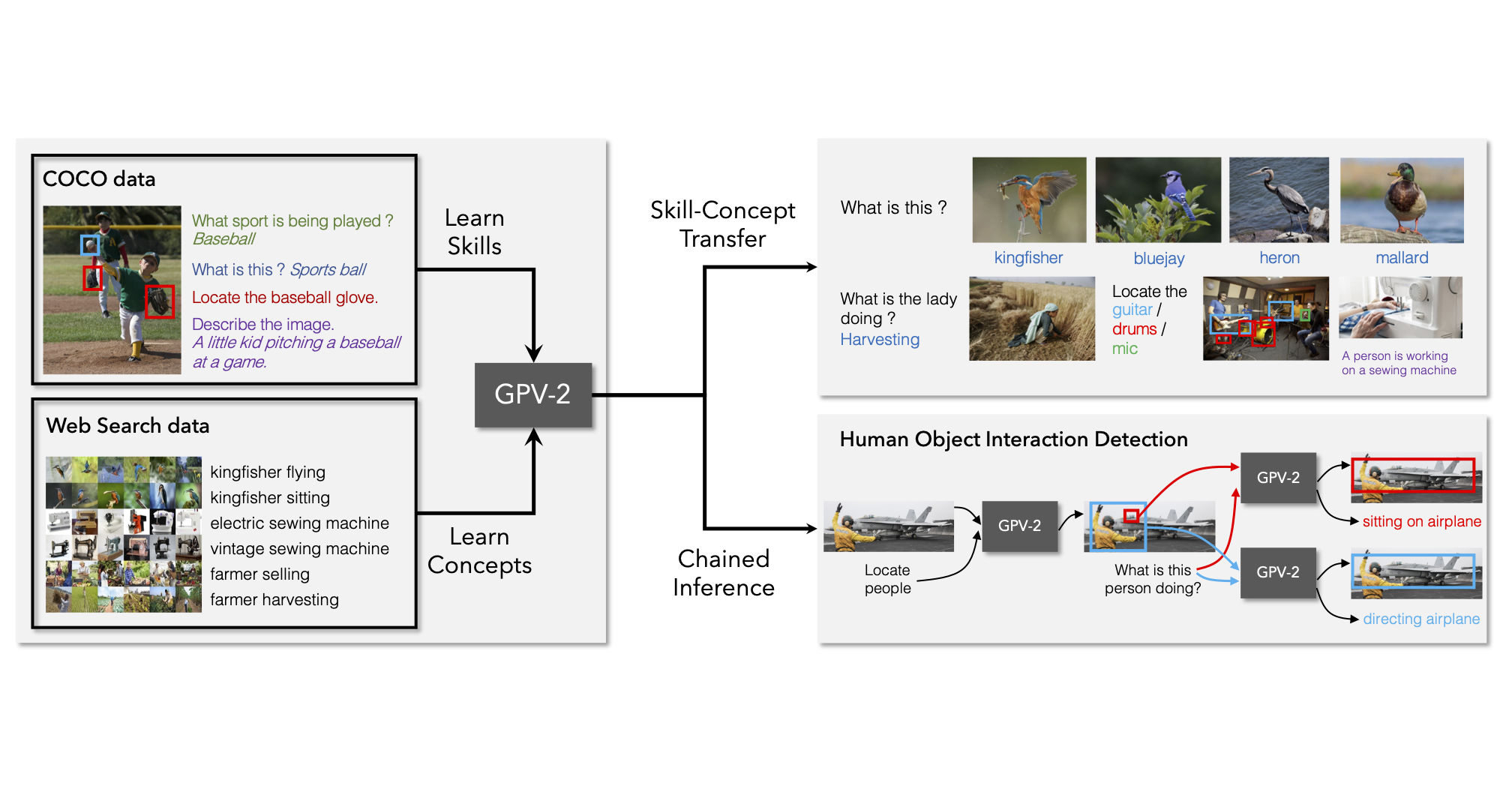
We propose expanding concept knowledge of general purpose vision systems by learning skills from supervised datasets while learning concepts from web image search data.
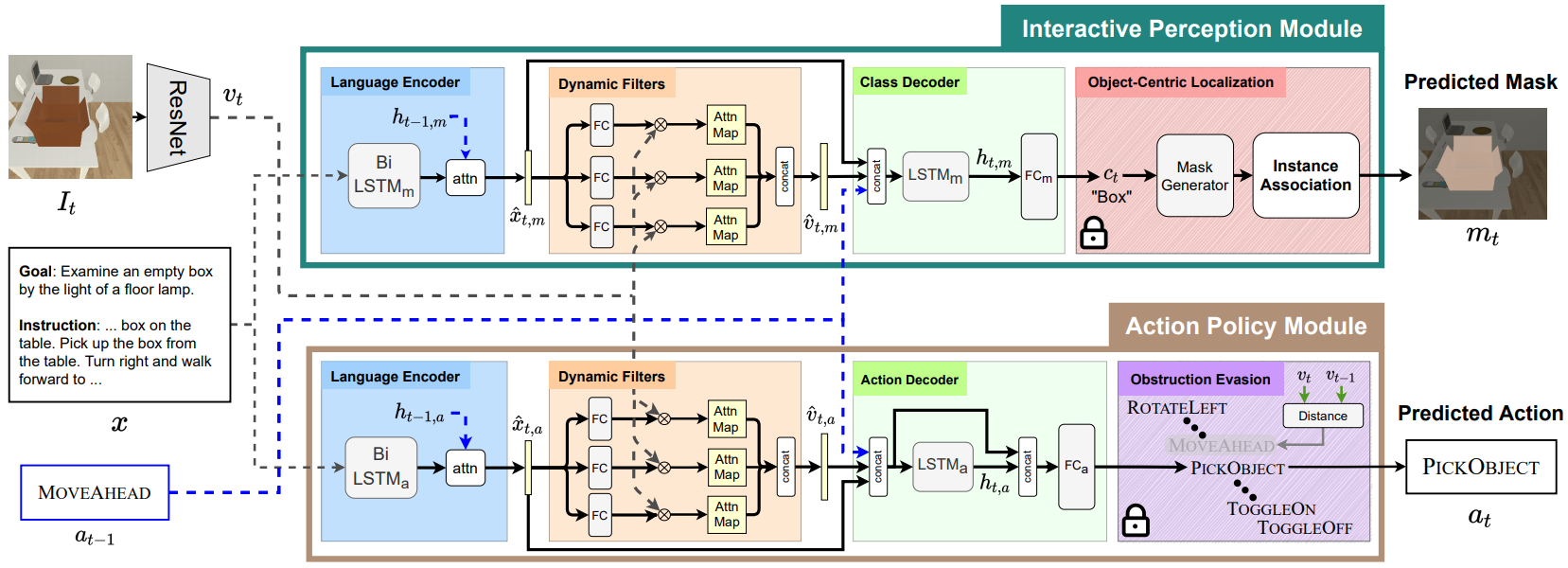
Modular Object-Centric Agent (MOCA) for interactive instruction following
Visual Representation Learning Benchmark for Self-Supervised Models
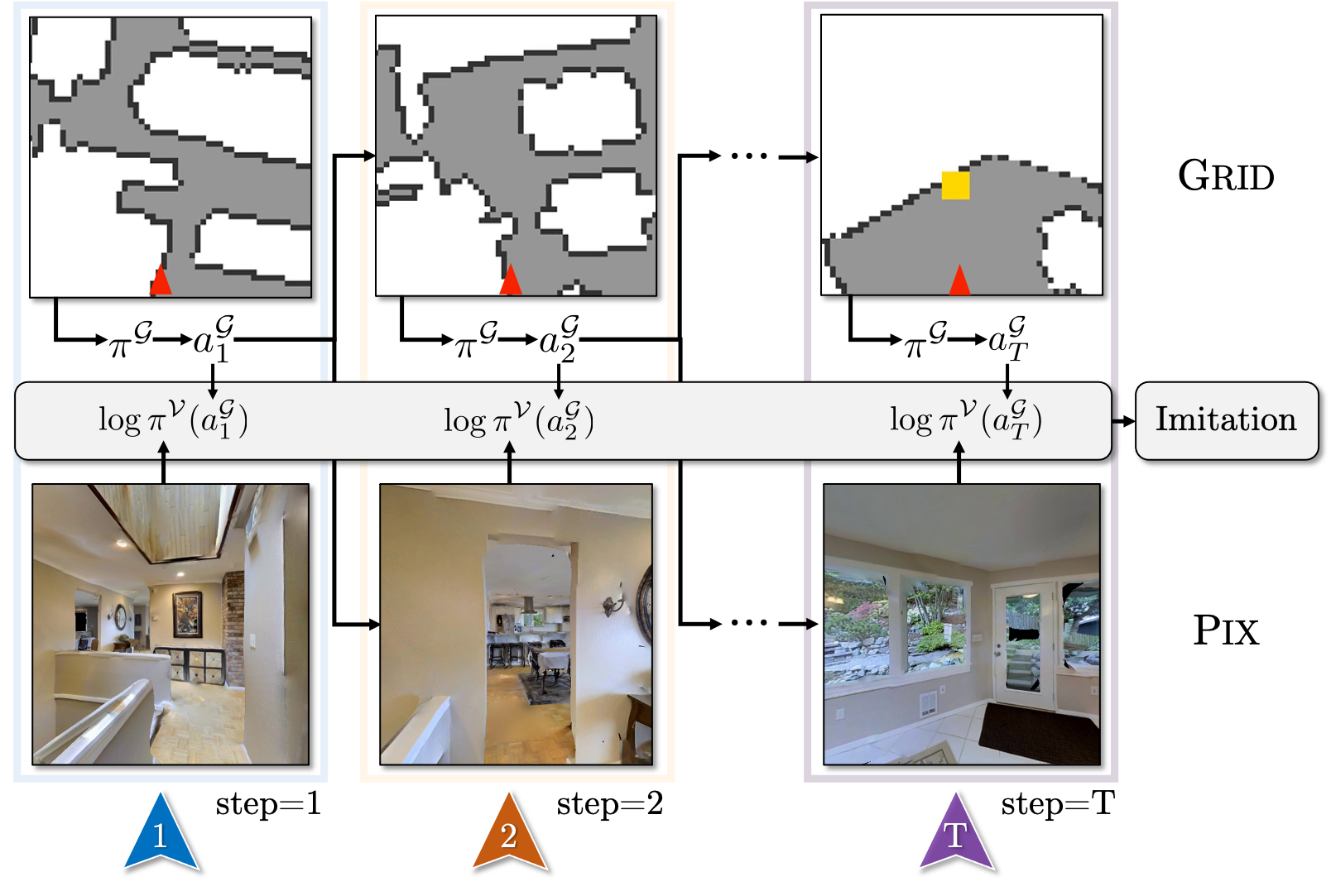
We show that one may train embodied agents with minimal supervision by transferring knowledge learned within gridworlds.
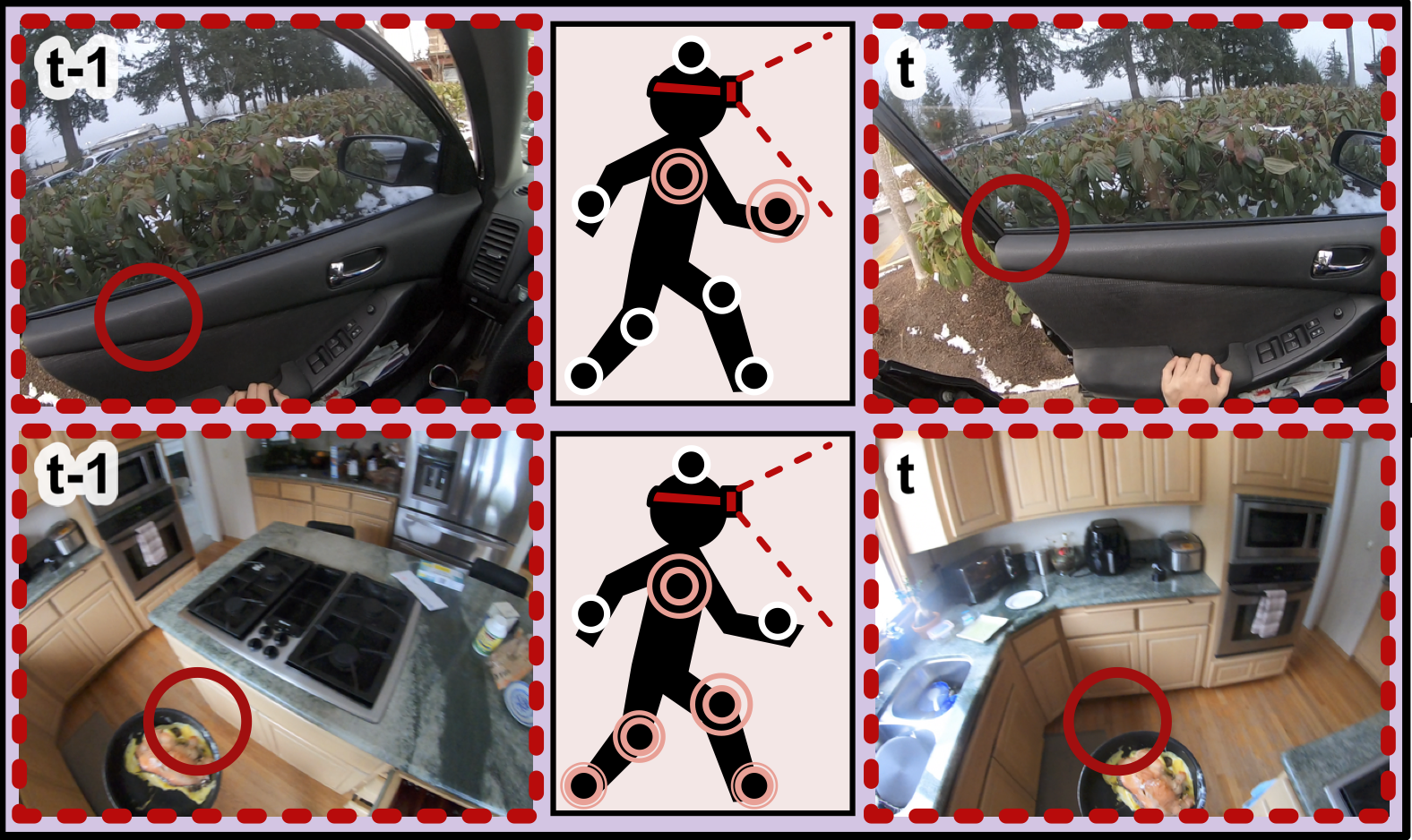

We use human interaction and attention cues to learn visual representations.
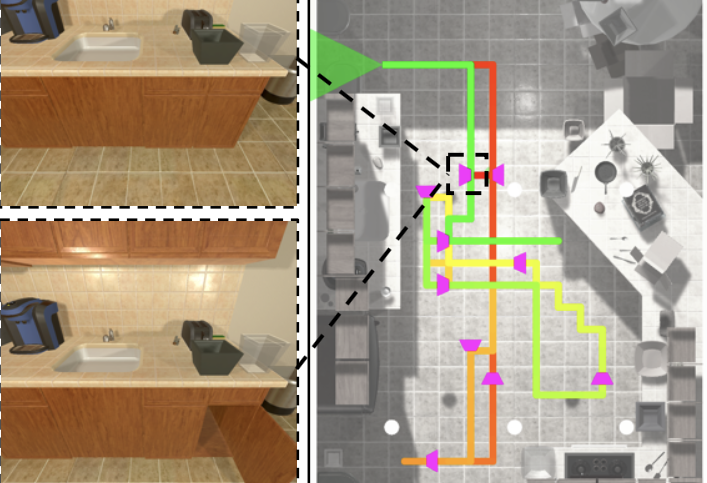
We study how interaction and play can be used as a new paradigm for training AI agents to understand their world.
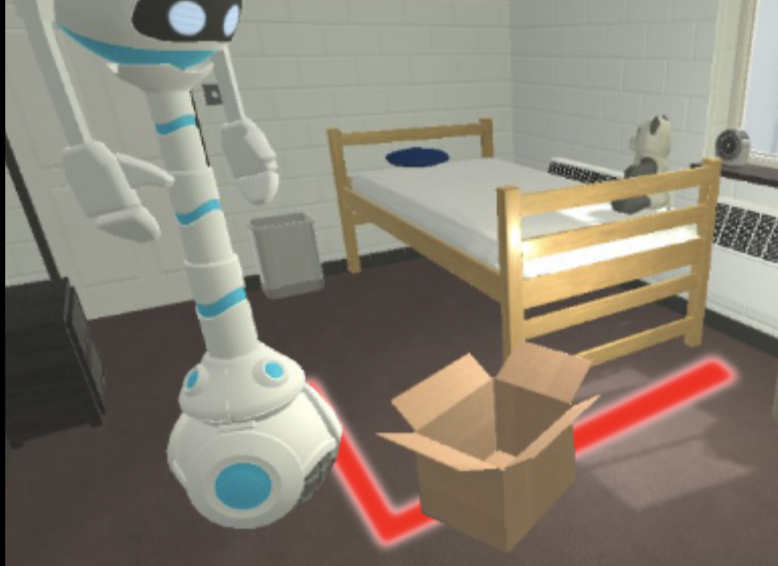

We study the problem of interactive navigation where agents learn to change the environment to navigate more efficiently to their goals.
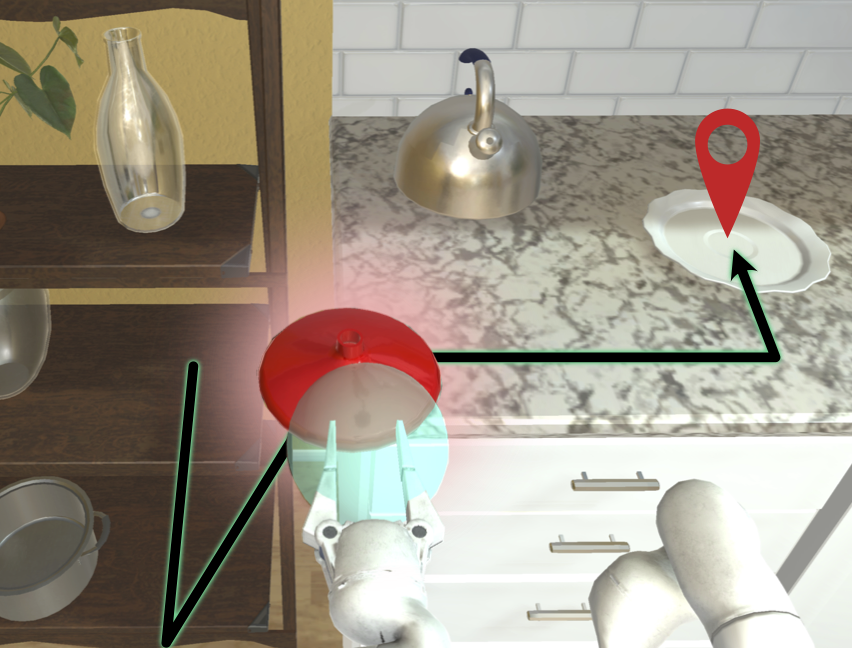

An interactive framework for low-level mobile object manipulation and navigation
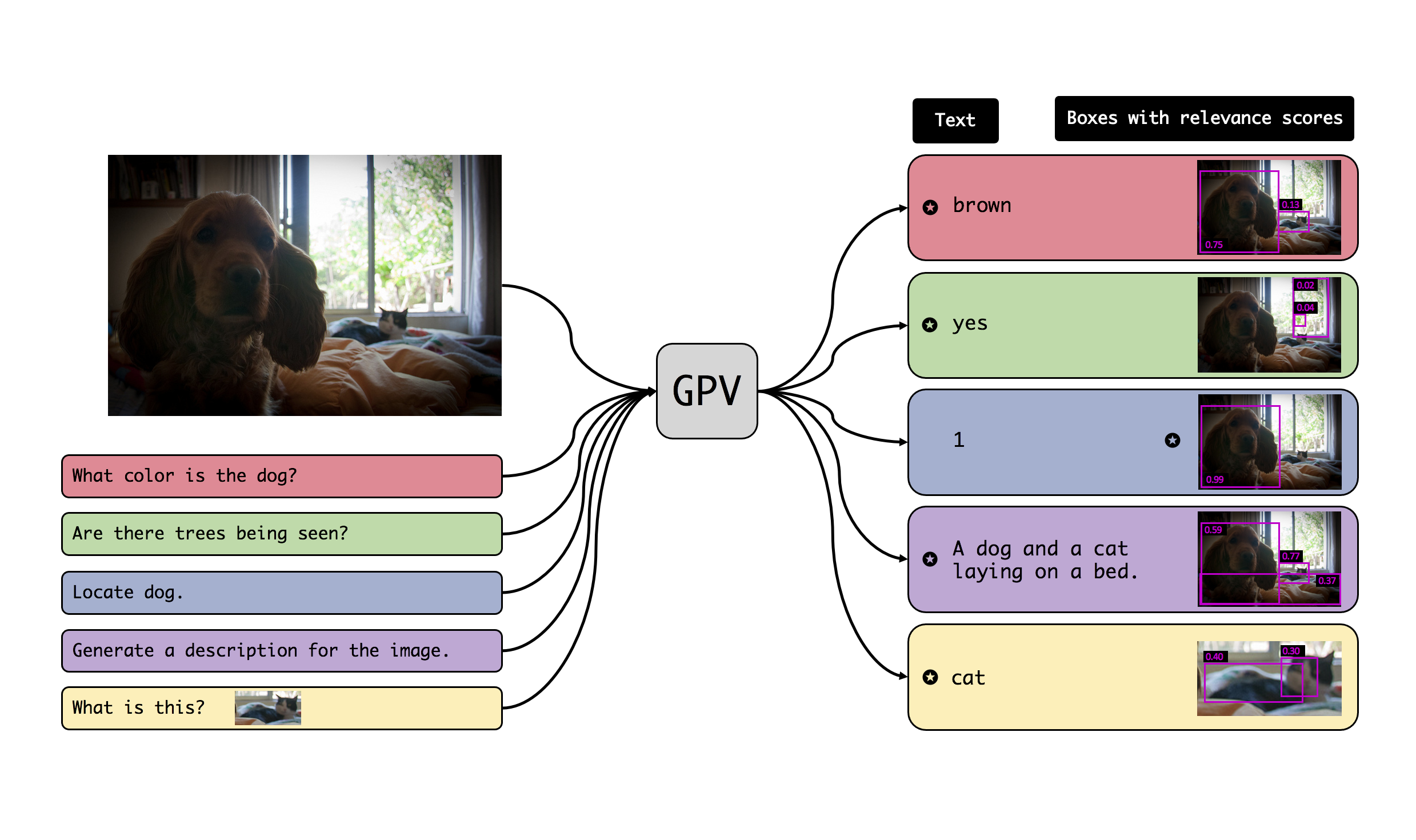
We propose a task-agnostic vision-language system that accepts an image and a natural language task description and outputs bounding boxes, confidences, and text.
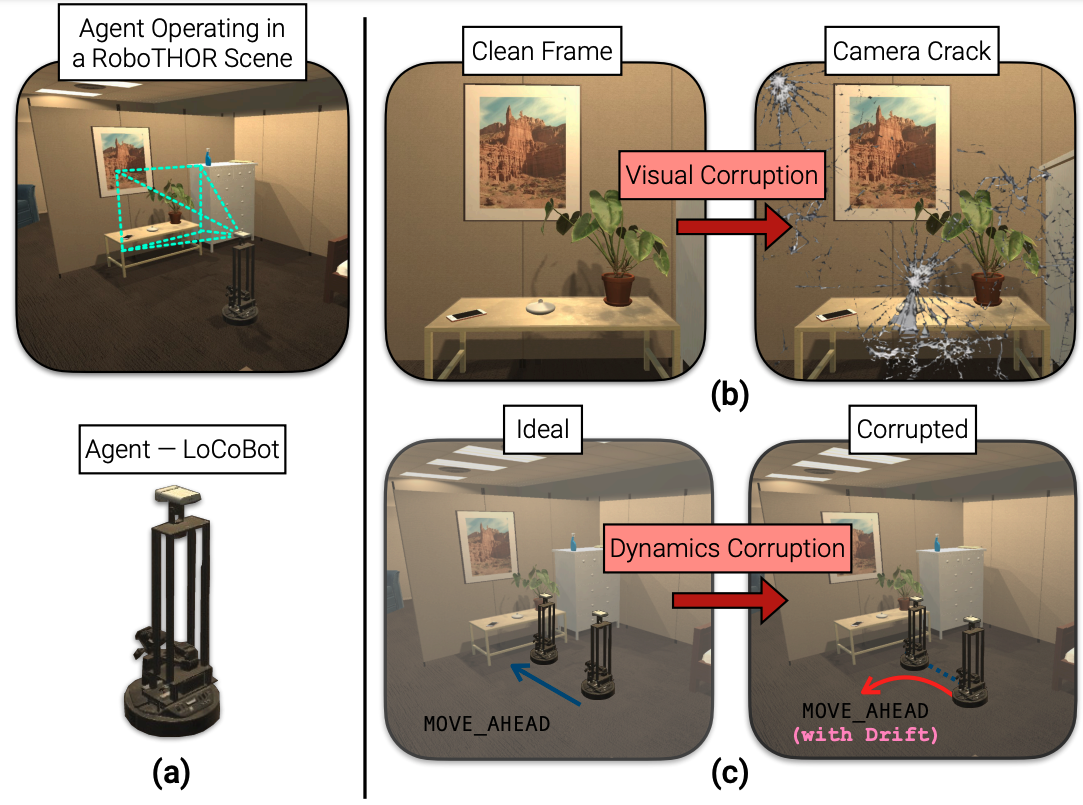
As an attempt towards assessing the robustness of embodied navigation agents, we propose RobustNav, a framework to quantify the performance of embodied navigation agents when exposed to a wide variety of visual and dynamics corruptions.
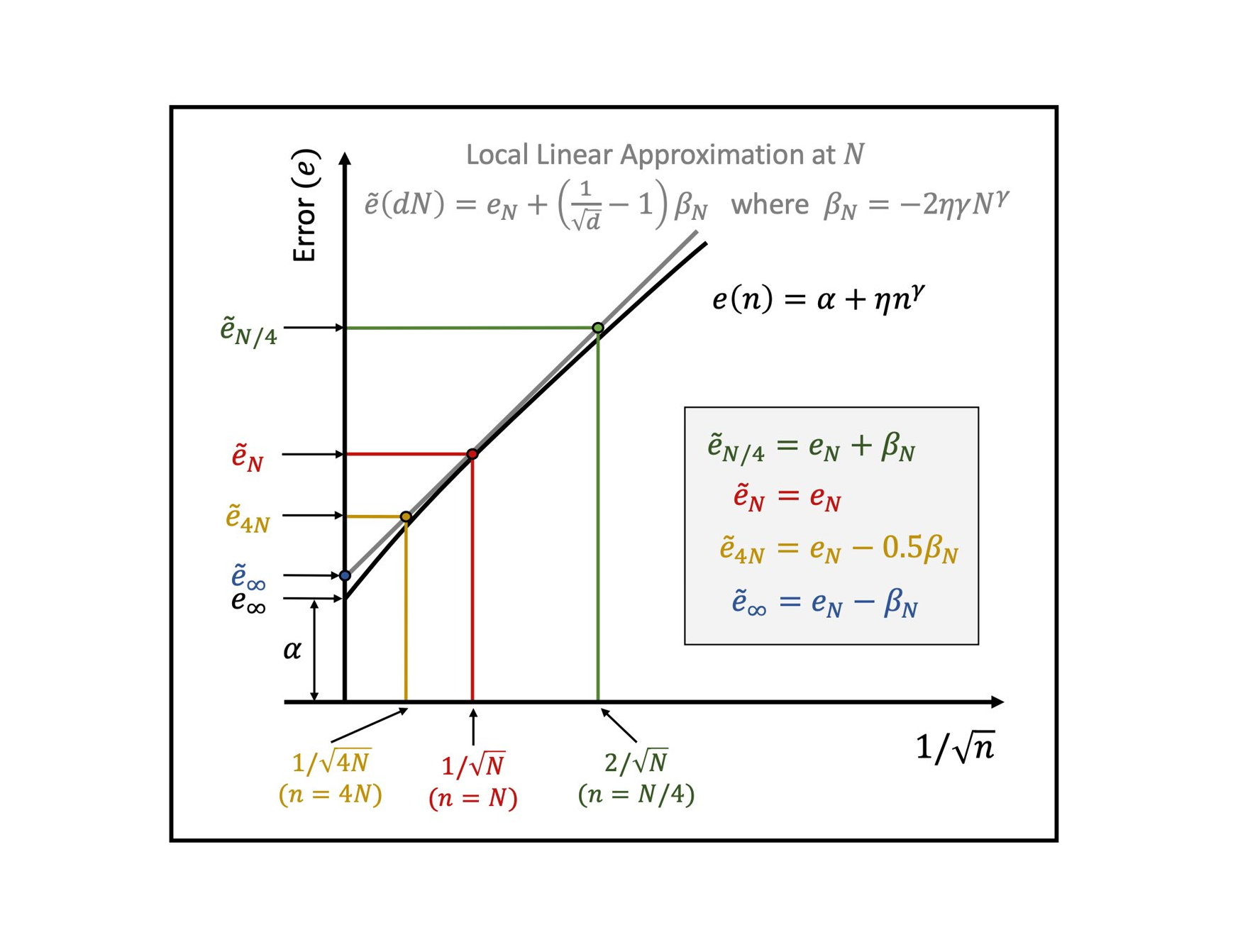
We propose a method to robustly estimate learning curves, abstract their parameters into error and data-reliance, and exemplify use of learning curves for classifier analysis.
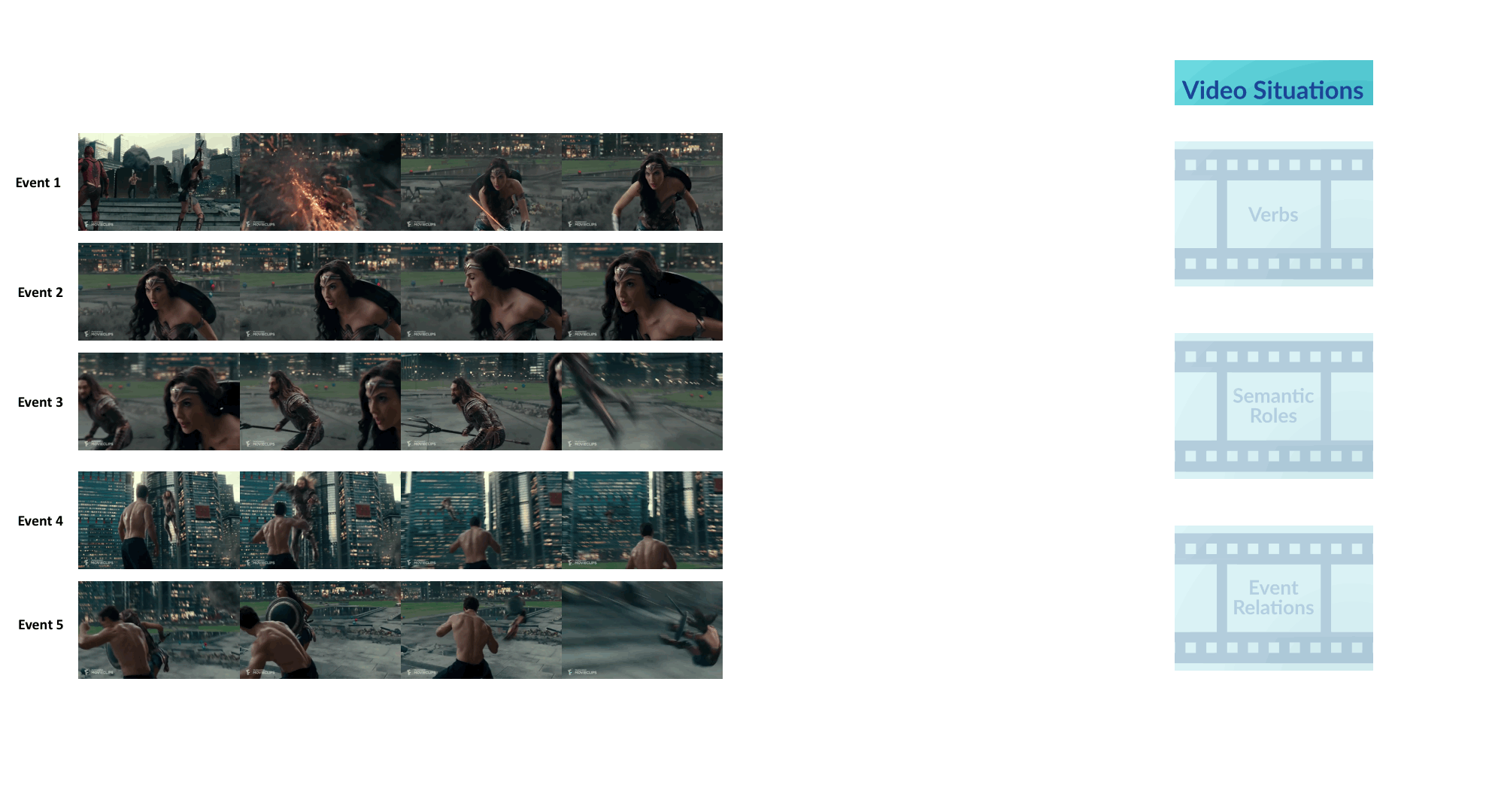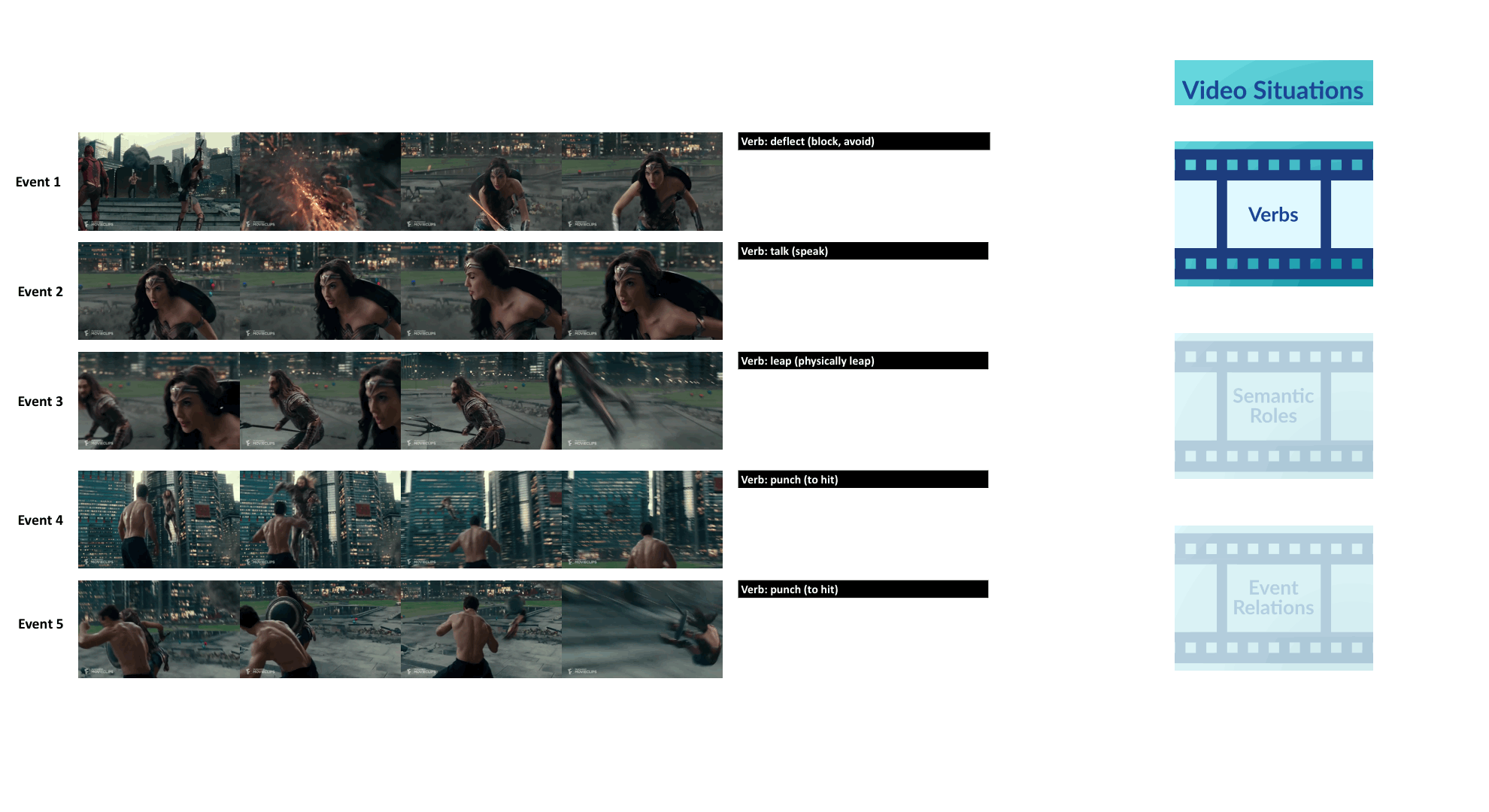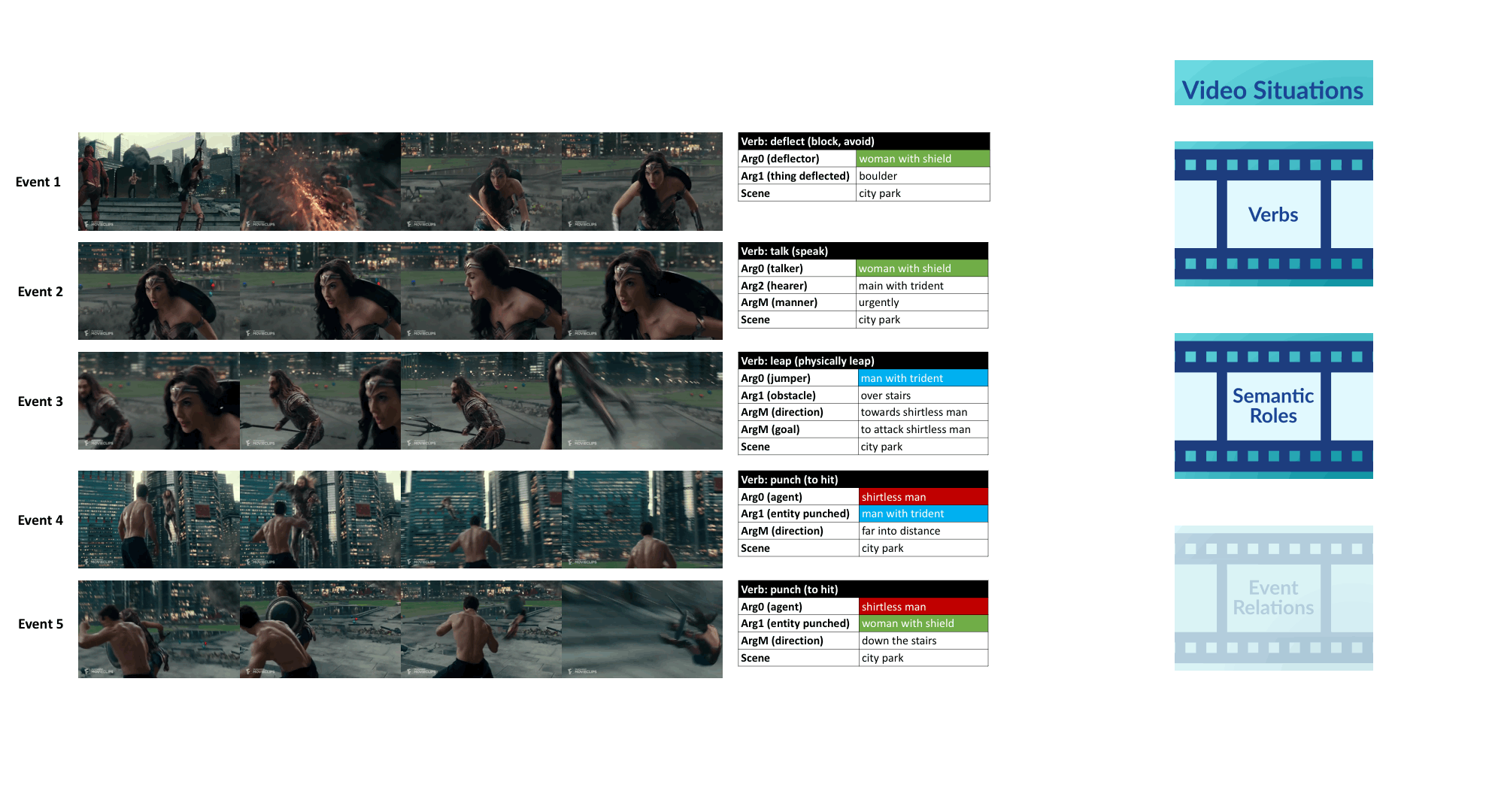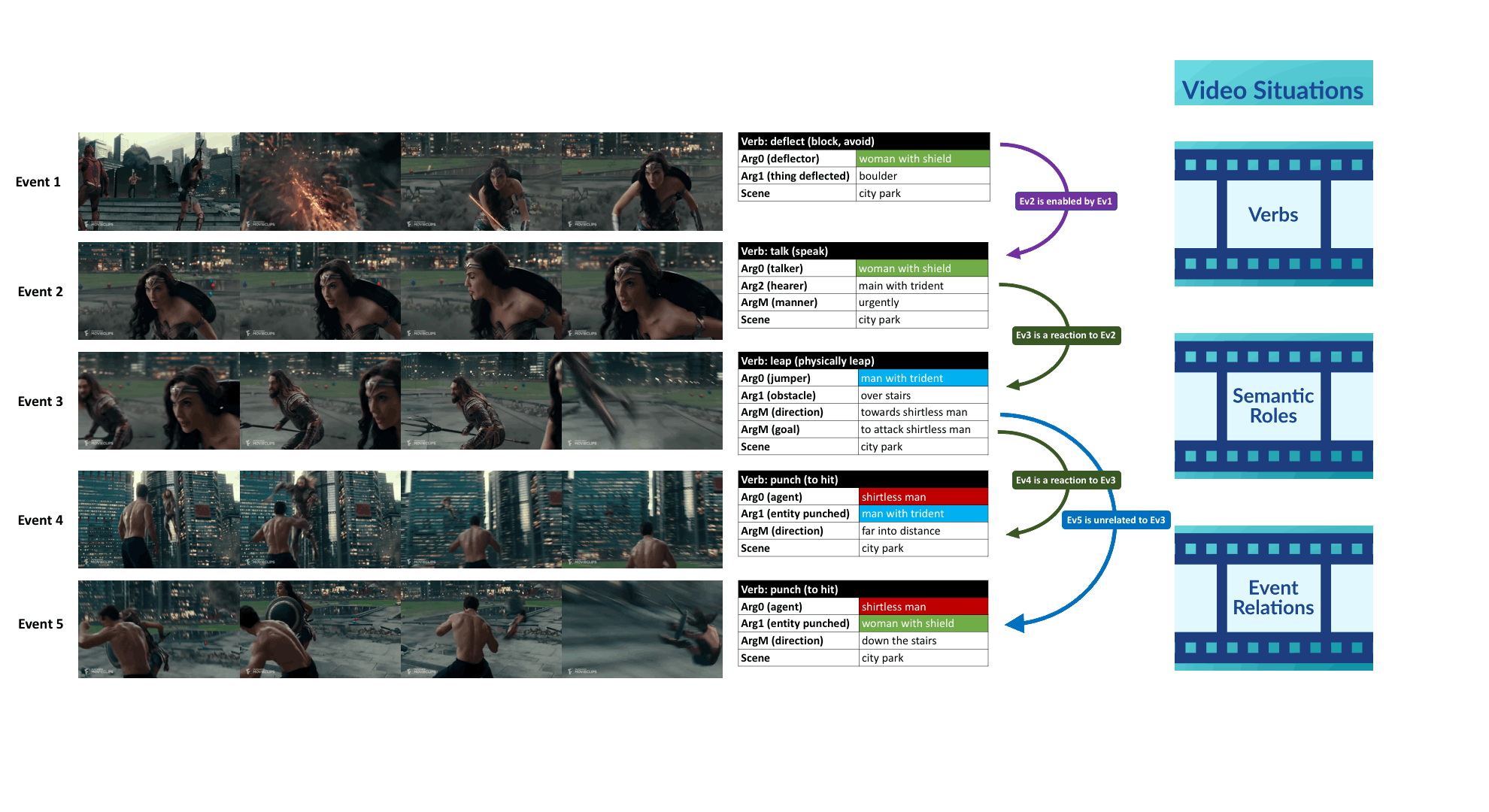
We introduce VidSitu, a large-scale movie dataset and the VidSRL task for representing complex situations using a semantic role labeling framework with coreferenced entities, and event-relations.
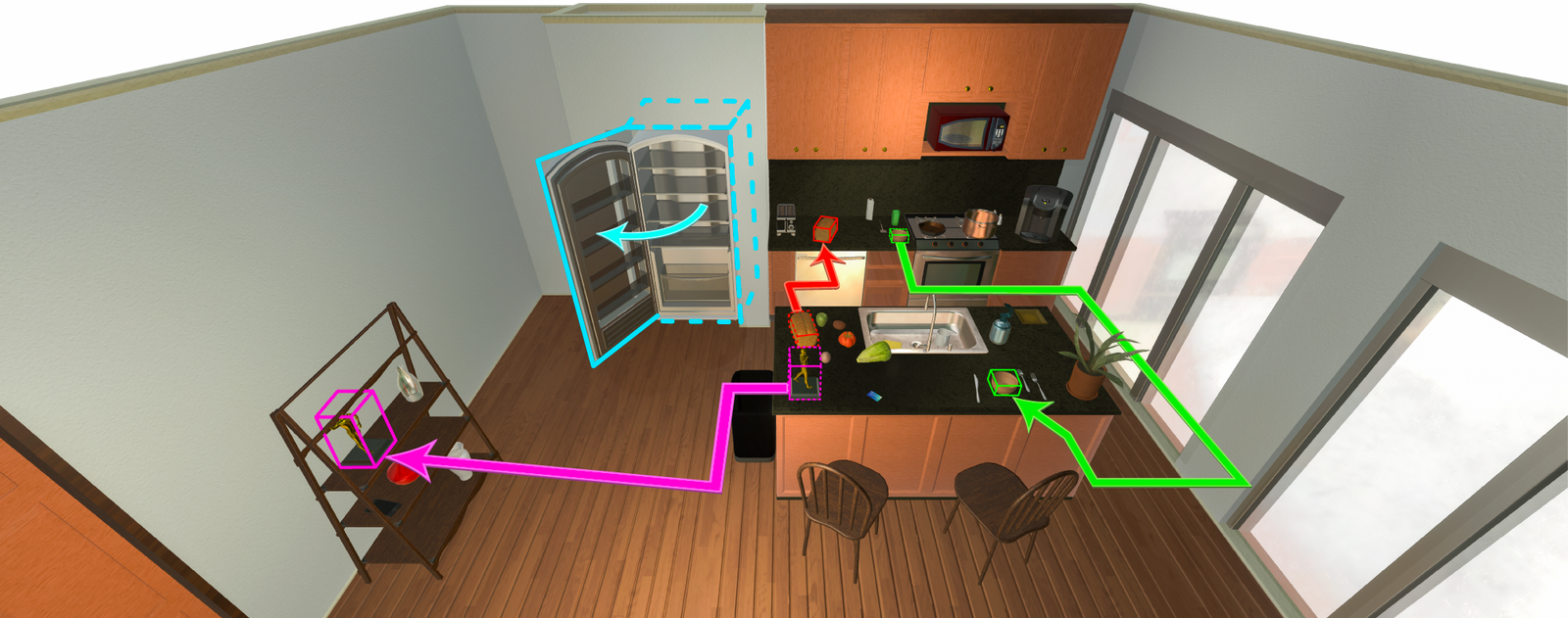
The goal of the AI2-THOR Rearrangement Challenge is to build a model/agent that move objects in a room, such that they are restored to a given initial configuration.
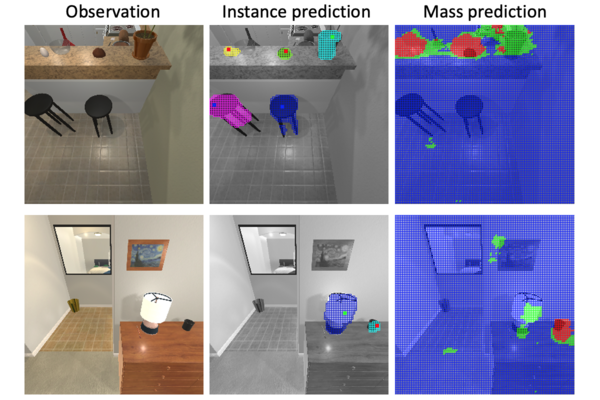
We learn object properties from interaction in a self-supervised manner

Paint, Caption and Answer Questions with Multi-Modal Transformers

An open source framework for research in Embodied-AI from AI2
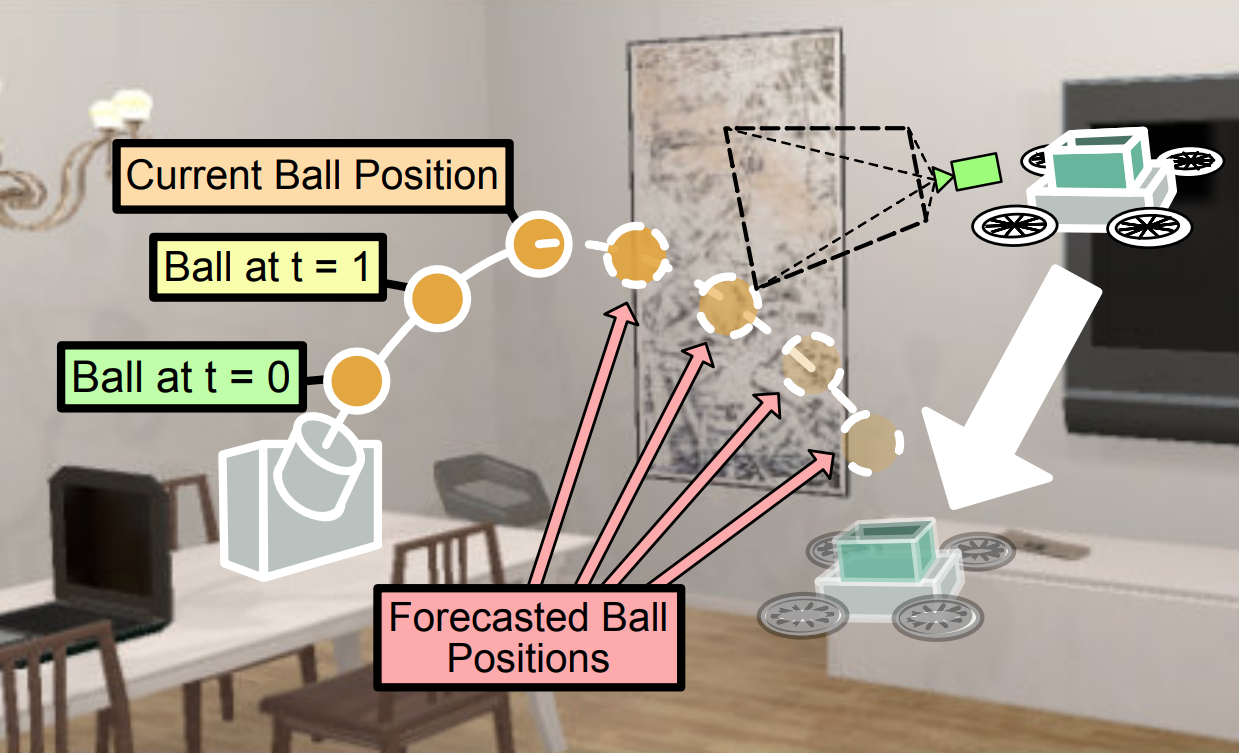
We study the problem of Visual Reaction, where the idea is to forecast the future and plan a sequence of actions accordingly.

A framework to study vision and language in the context of instruction following in an interactive environment.
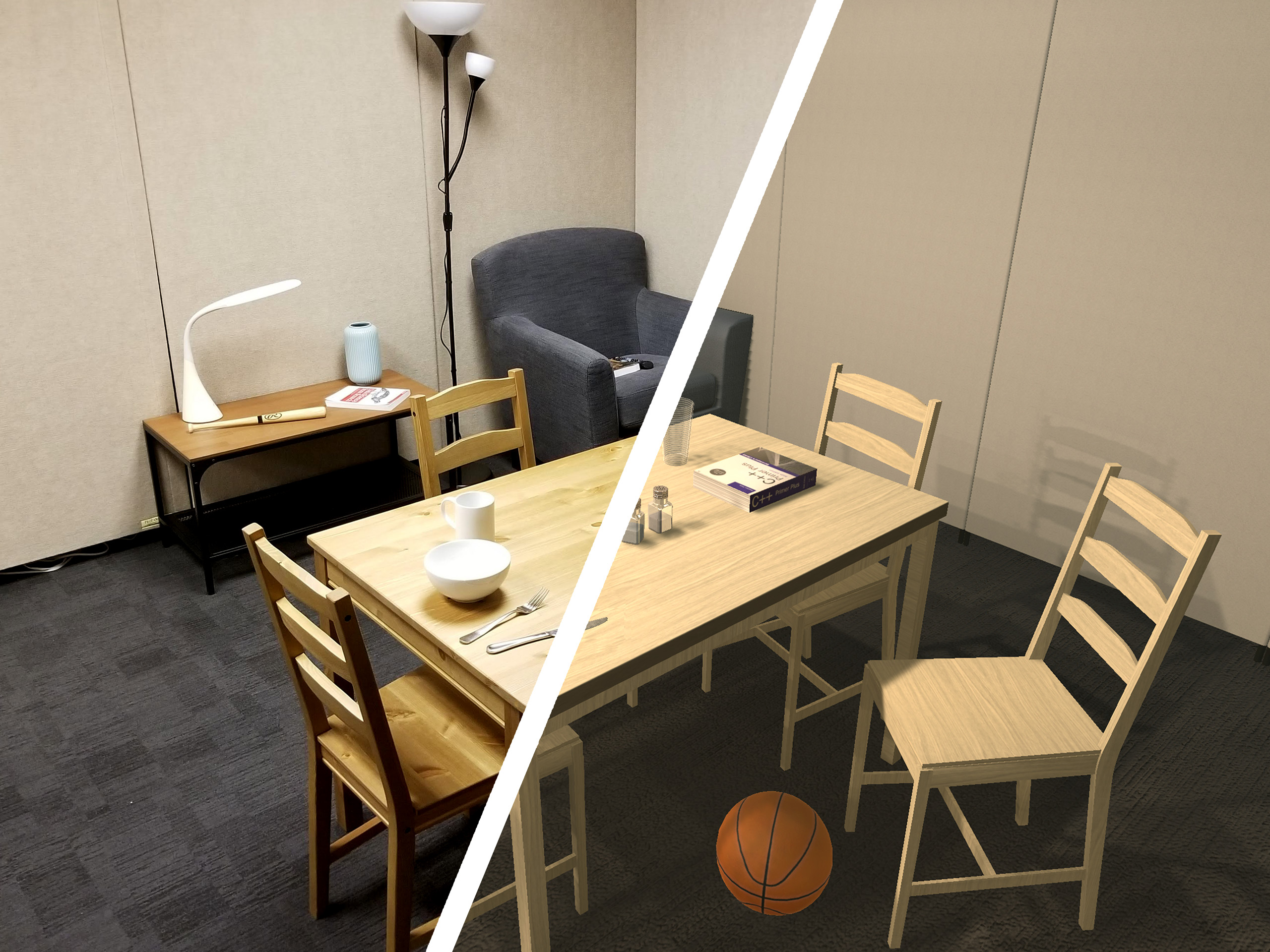

RoboTHOR is an environment within the AI2-THOR framework, designed to develop embodied AI agents. It consists of a series of scenes in simulation with counterparts in the physical world.

A dataset and model to describe images with the primary action in the image as well as labels and bounding boxes for the entities involved in the action.

Try out leading computer vision models on a variety of tasks.

A dataset that includes questions that require outside knowledge to be answered.
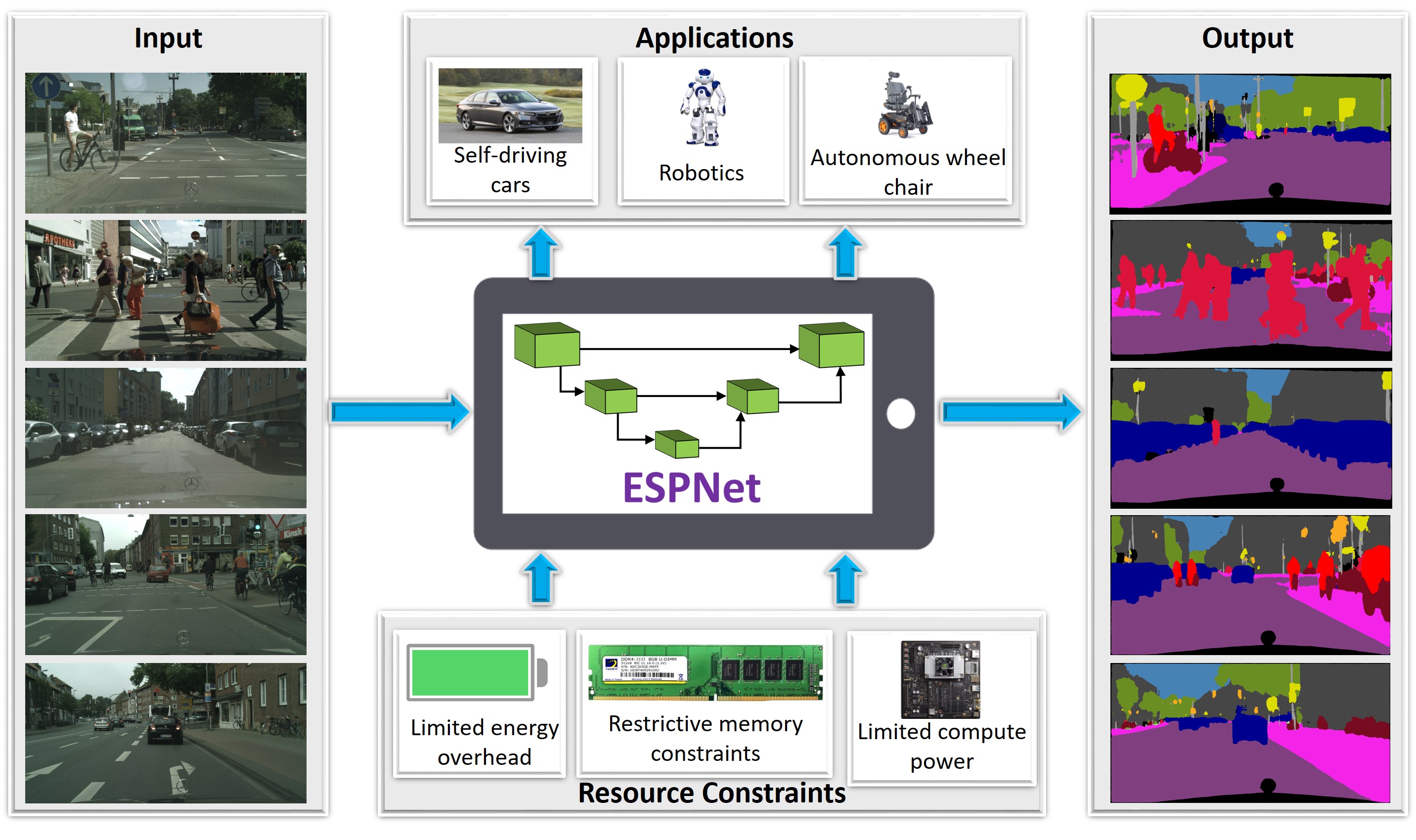
This project explores efficient CNN designs for different computer vision tasks including object classification, object detection, and semantic segmentation.
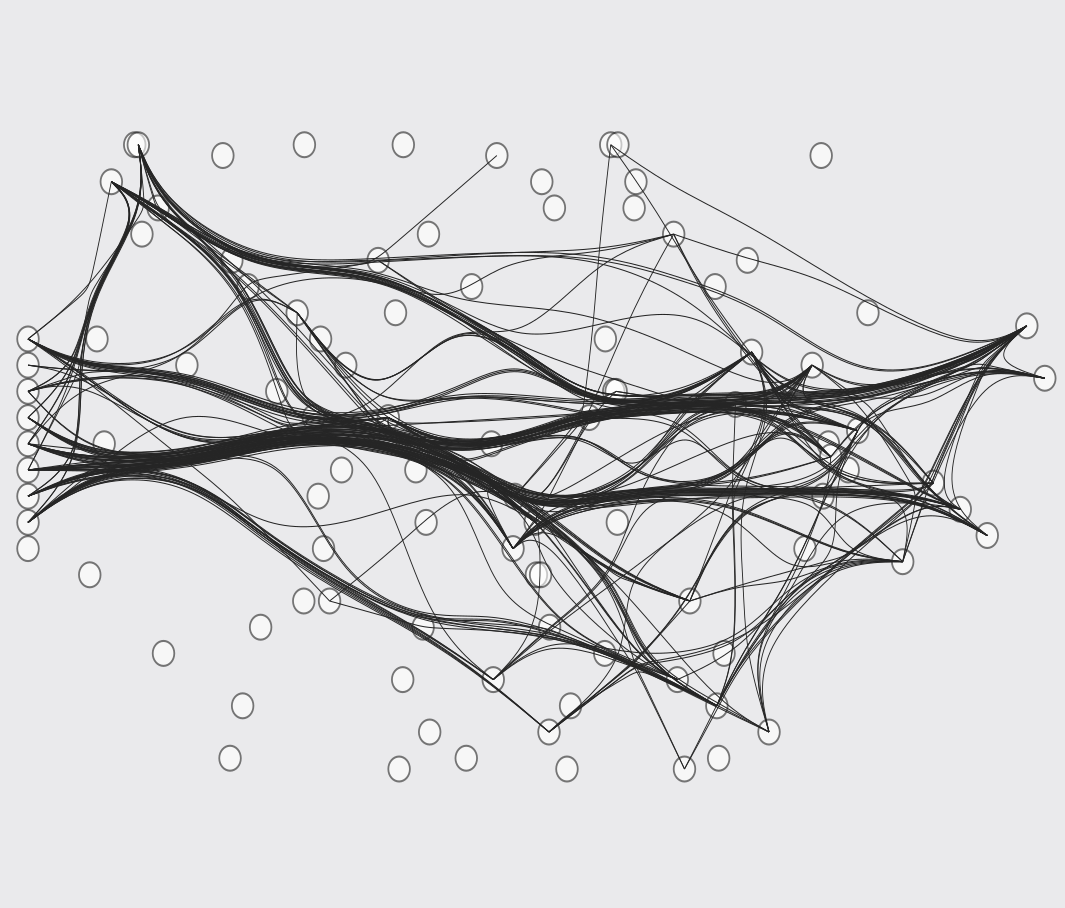
We propose a method for discovering neural wirings. The wiring of our network is not fixed during training, as we learn the network parameters we also learn the network structure itself.
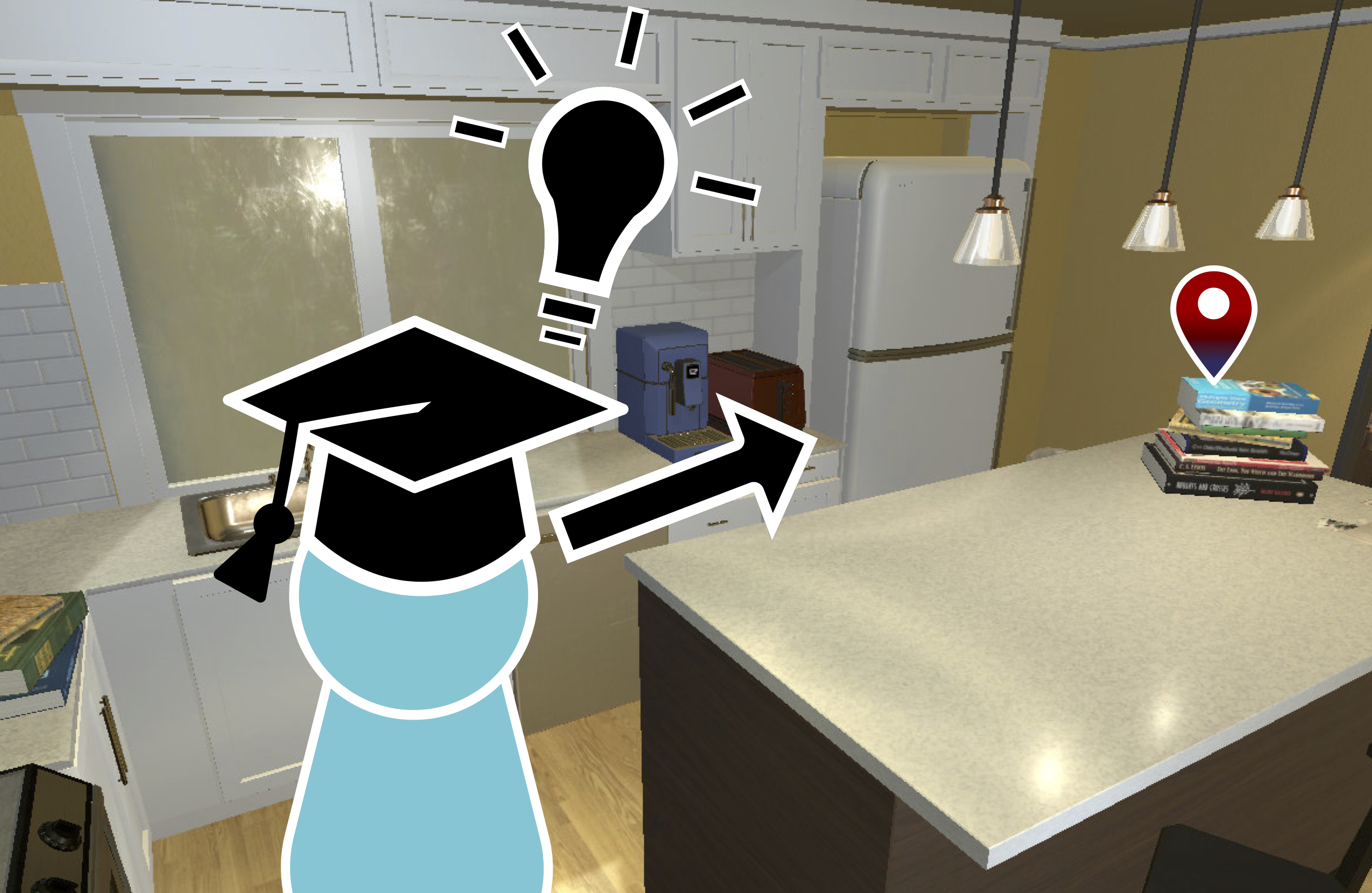

We introduce a navigation agent that learns to adapt to its environment through self-supervised interaction.

This project explores modeling scale variations by learnable dynamic scaling policies. We observed consistent improvements on ImageNet classification, and other downstream vision tasks.
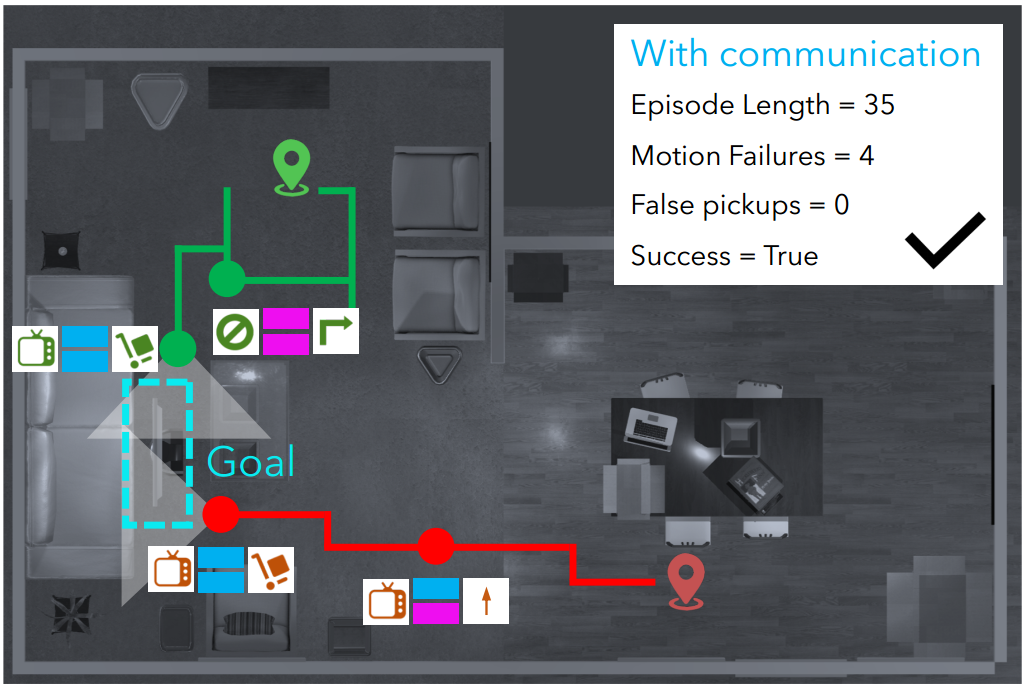
Learning to collaborate in visual environments and demonstrate the benefits of learned explicit and implicit communication to aid task completion. We also provide a statistical interpretation of the communication strategy learned by the agents.
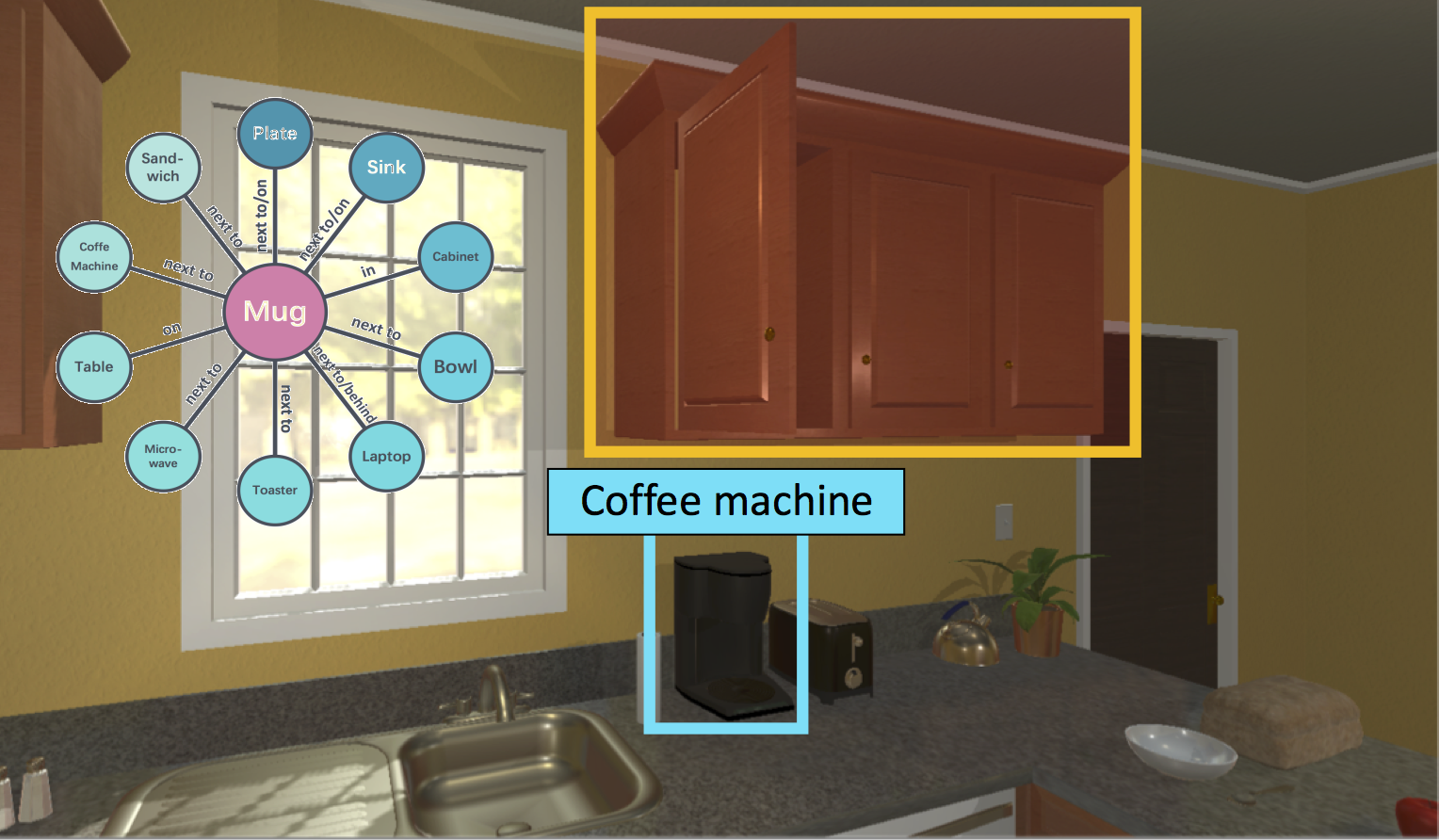
The goal is to augment an RL-based method with a knowledge graph to better navigate in novel scenes and towards unseen objects.
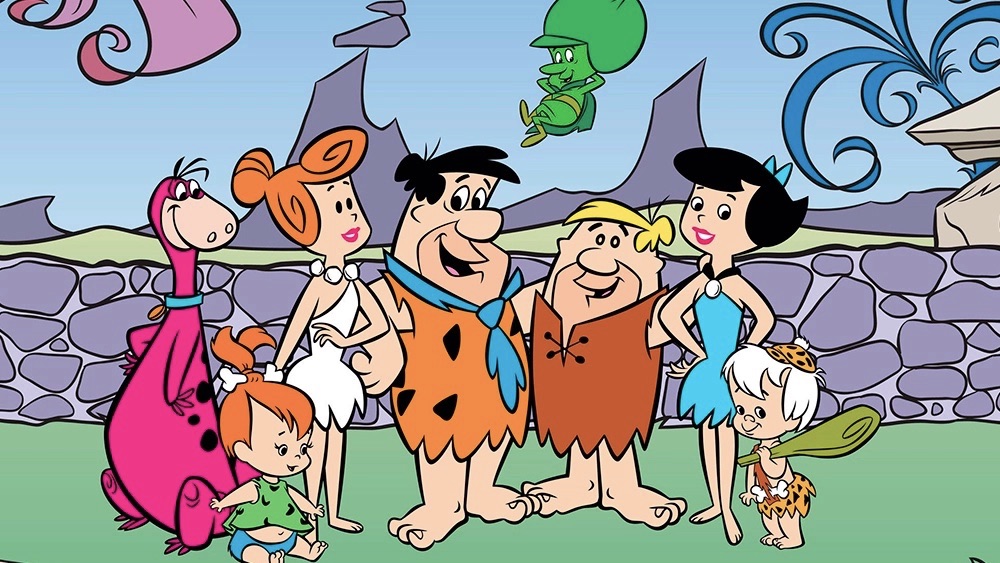

Given a scene description, Composition, Retrieval and Fusion Network (CRAFT) predicts a layout of mentioned entities, retrieves spatio-temporal entity segments from a video database and fuses them to generate scene videos. Results are shown on a new FLINTSTONES dataset.
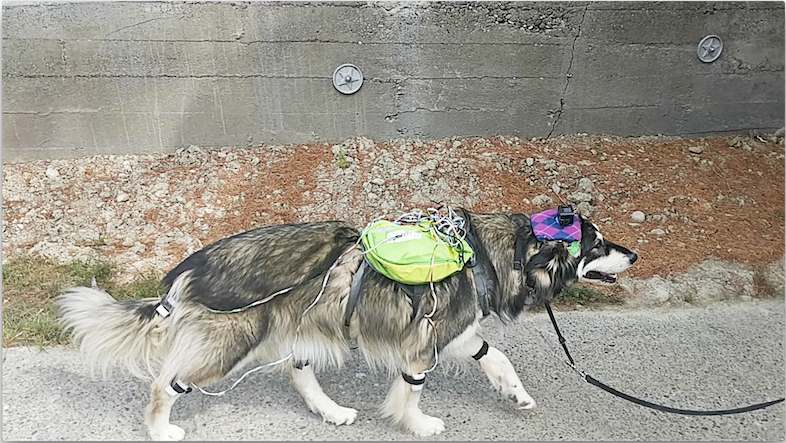

This project explores directly modeling a visually intelligent agent. Our model inputs visual information and predicts the agent's actions. We demonstrate our model on DECADE, a large-scale dataset of ego-centric videos from a dog's perspective.
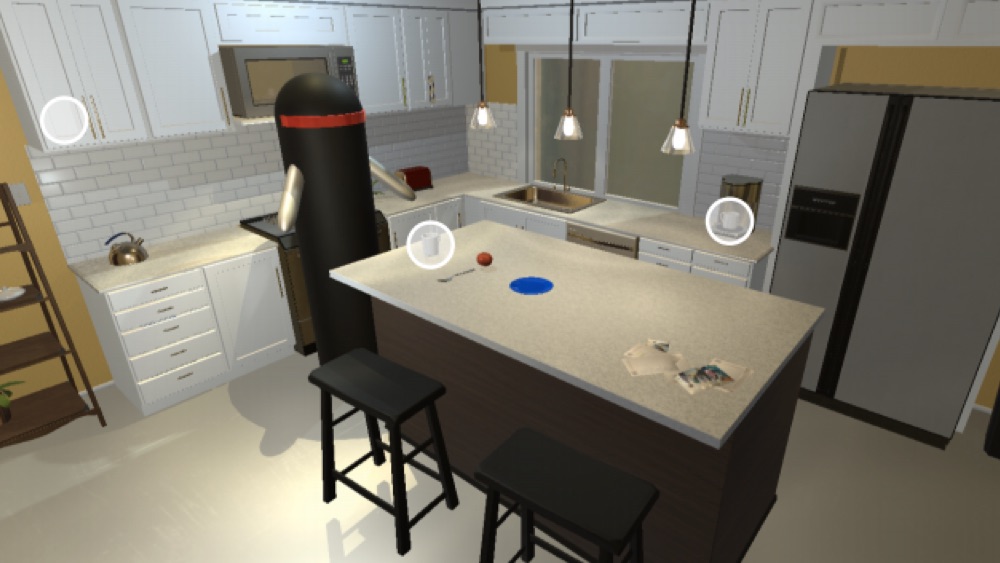

This project explores Interactive Question Answering (IQA), the task of answering questions such as 'Are there any apples in the fridge ?' that require an autonomous agent to interact with a dynamic visual environment.
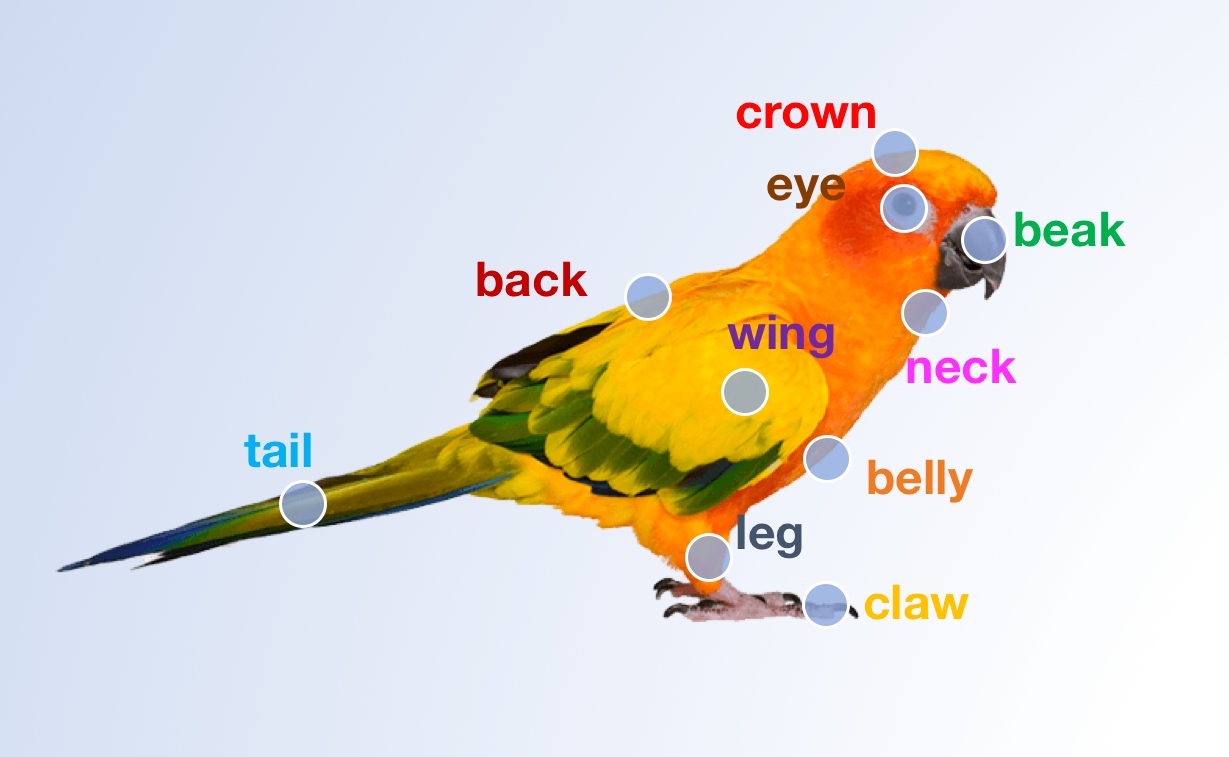
This project addresses the problem of understanding diagrams in the absence of large labelled datasets, by transferring labels from smaller labeled datasets of diagrams (within-domain) as well as from labeled datasets of natural images (cross-domain).

MotifNet is a model for creating graph representations images, scene graphs. In scene graphs, every object is a node and relationships between objects are edges. MotifNet captures high-order, global repeating structures in such graphs, motifs.

SeGAN is a model for generating the occluded regions of objects, where a GAN first generates the shape and then the appearance of the invisible regions.
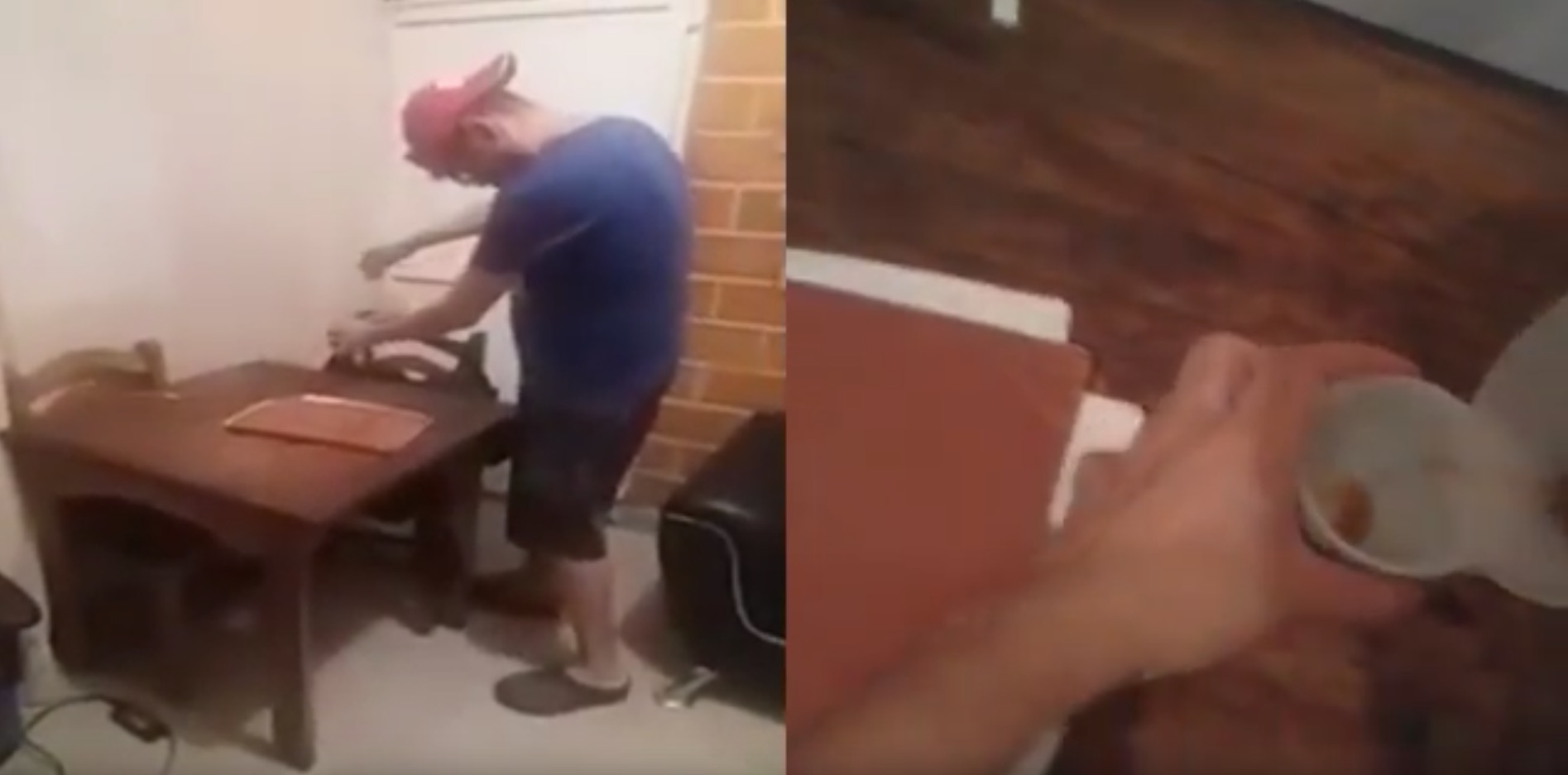

Charades-Ego is a dataset that guides research into unstructured video activity recogntion and commonsense reasoning for daily human activities with paired videos of first person and third person perspective.

A combination of Deep Reinforcement Learning and Imitation Learning to plan a sequence of actions for performing tasks.
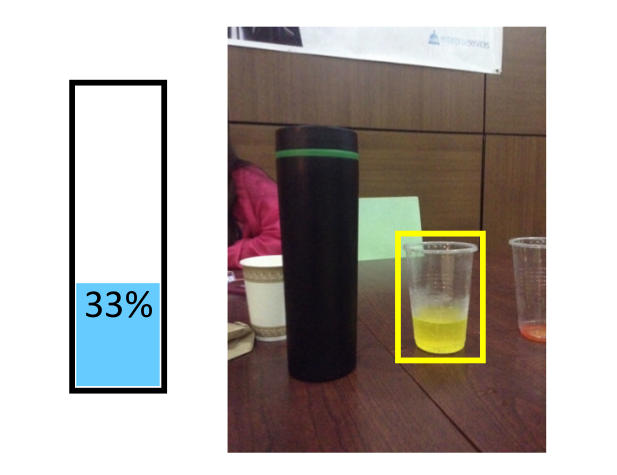
Understanding the dynamics of liquids and their containers. The aim is to estimate the volume of containers, infer the amount of liquid, and predict pouring behavior.
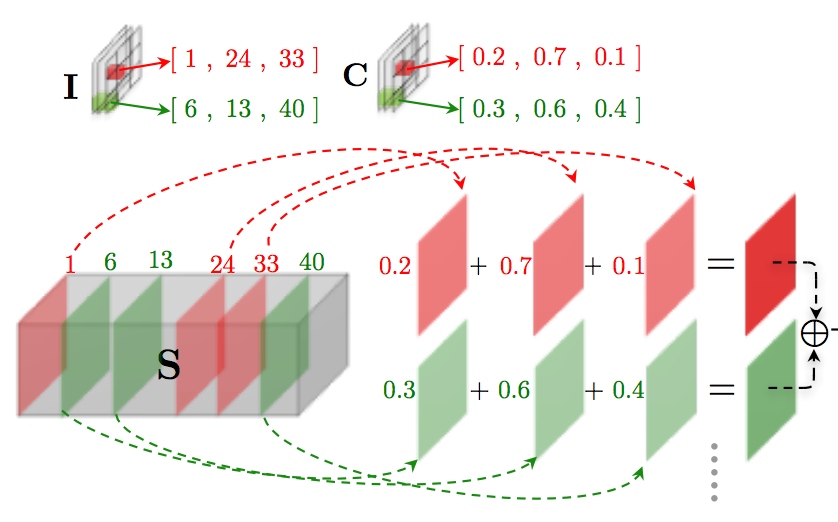
The LCNN improves the efficiency of the convolutional neural networks by learning a dictionary and a small set linear weights of them and using a look up for inference.
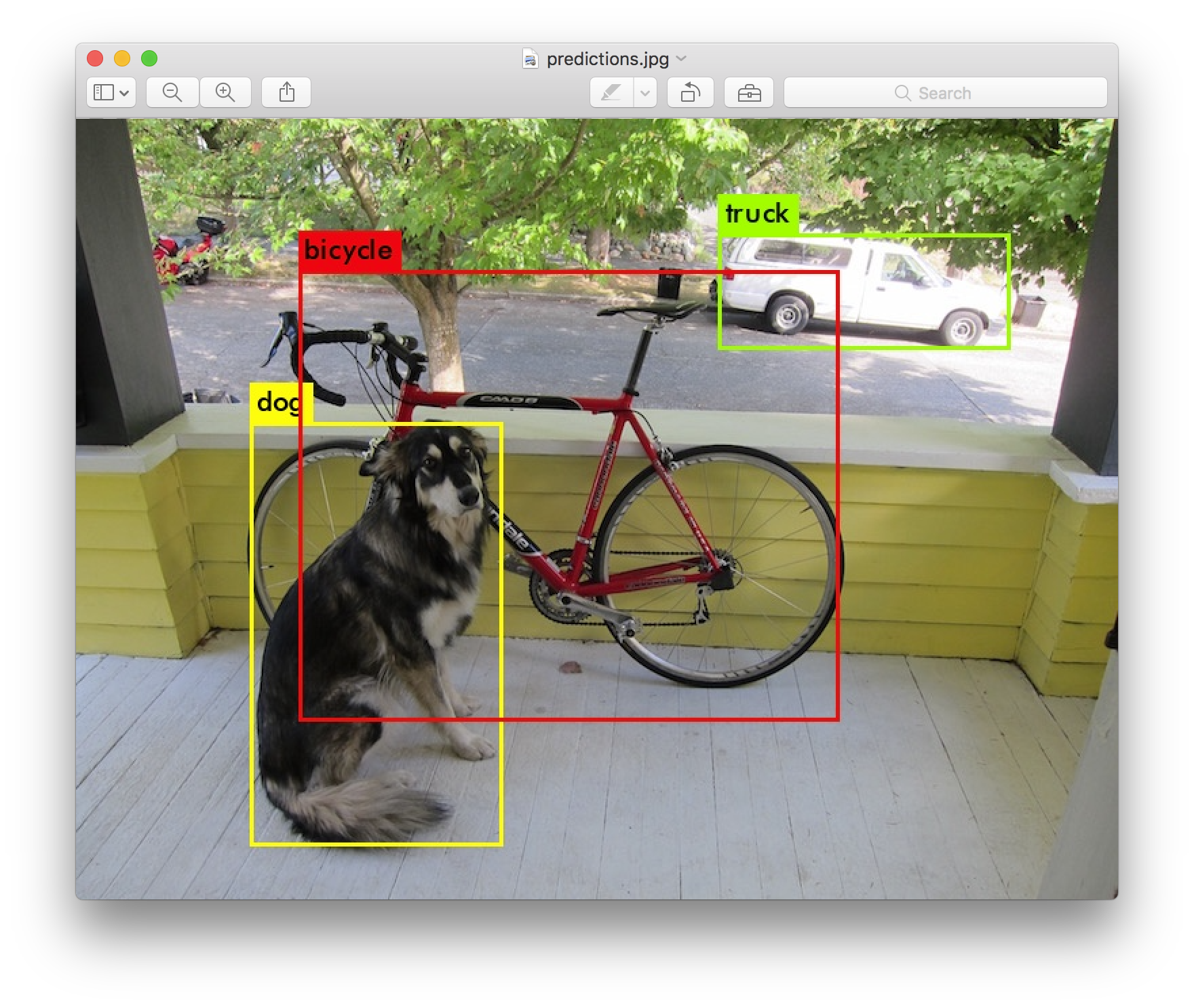
You only look once (YOLO) is a state-of-the-art, real-time object detection system.

imSitu is a dataset supporting Situation Recognition, the problem of producing a concise summary of the situation an image depicts. Events (such as feeding) are described by verbs, objects and semantic roles defining how the objects are particpating.
TQA is a machine comprehension dataset that pairs middle school science questions with the supporing textbook material (including diagrams) needed to answer them.

Deep Reinforcement Learning for the task of visual navigation. The goal is developing a more efficient and generalizable Reinforcement Learning approach.
Bi-directional Attention Flow (BiDAF) network is a multi-stage hierarchical process that represents context at different levels of granularity and uses a bi-directional attention flow mechanism to achieve a query-aware context representation without early summarization.
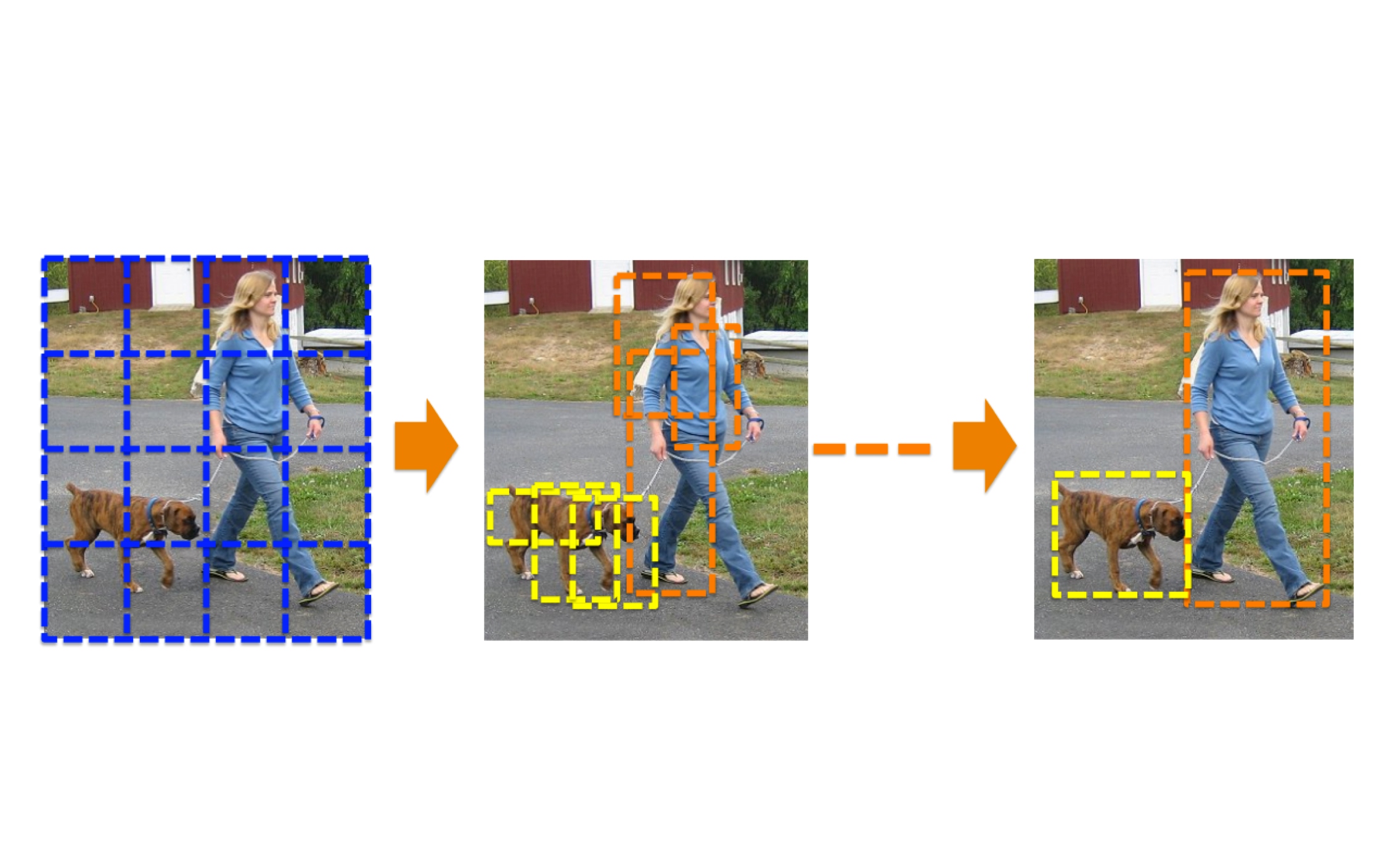
The G-CNN improves the precision of bounding box by regressing the location and scale of the bounding box iteratively.
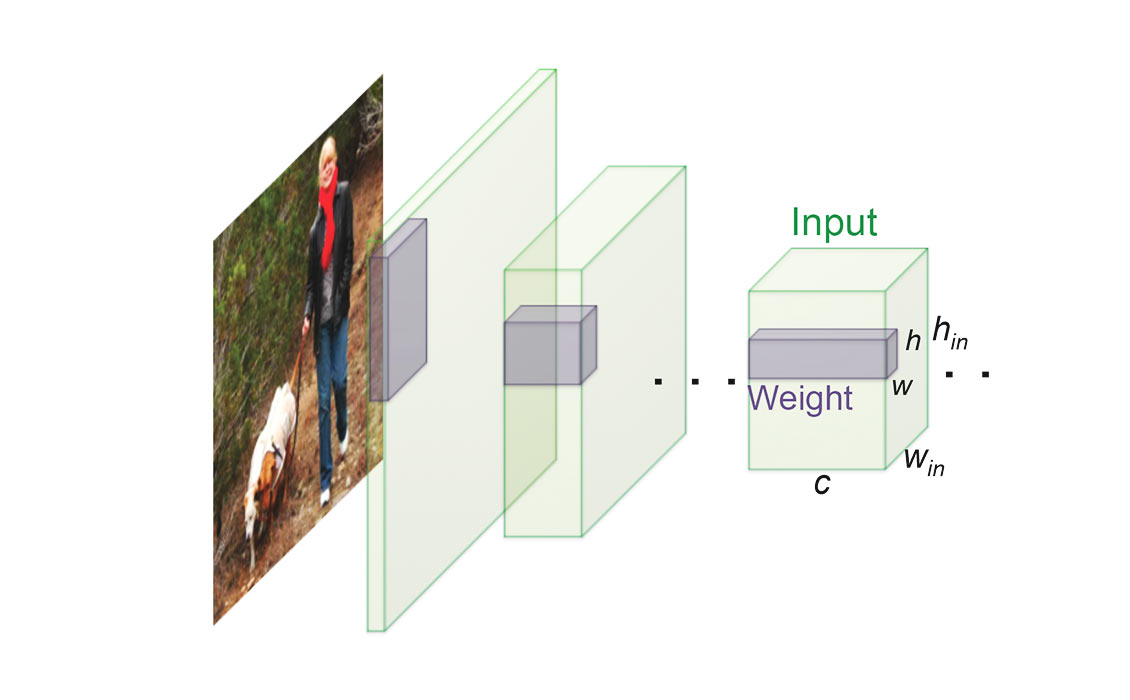
This project aims at improving the efficiency of the convolutional neural networks by using the binary precision operations.
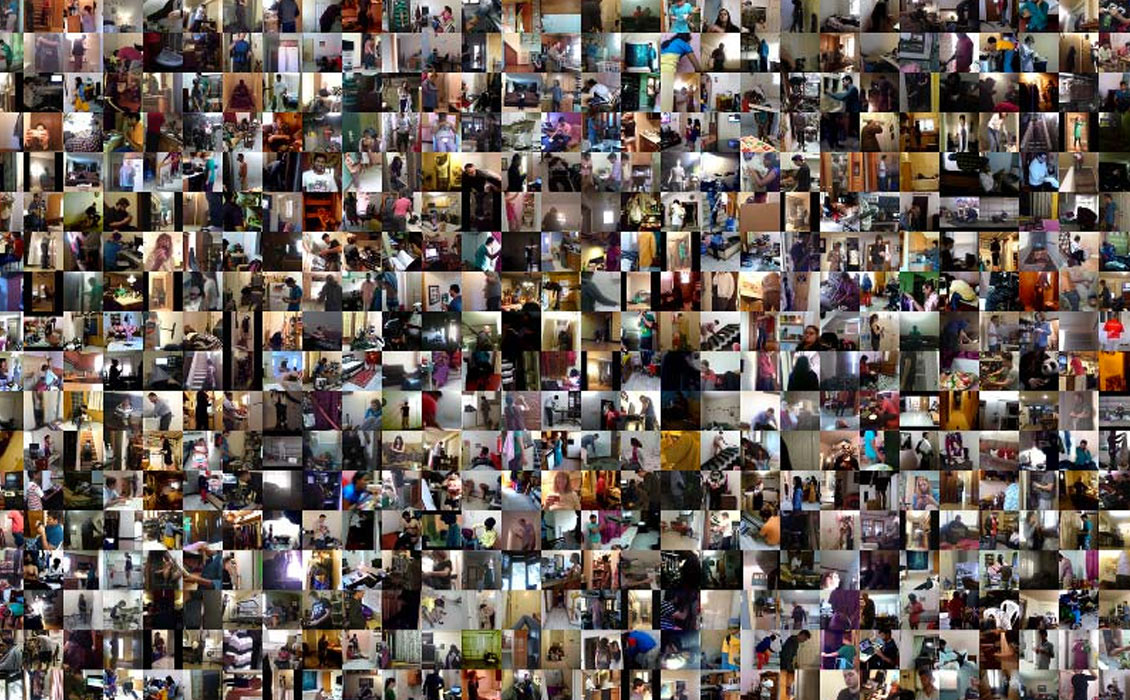
Charades is a dataset that guides research into unstructured video activity recogntion and commonsense reasoning for daily human activities.
Predicting movements of objects via estimation of scene geometry and its underlying physics.
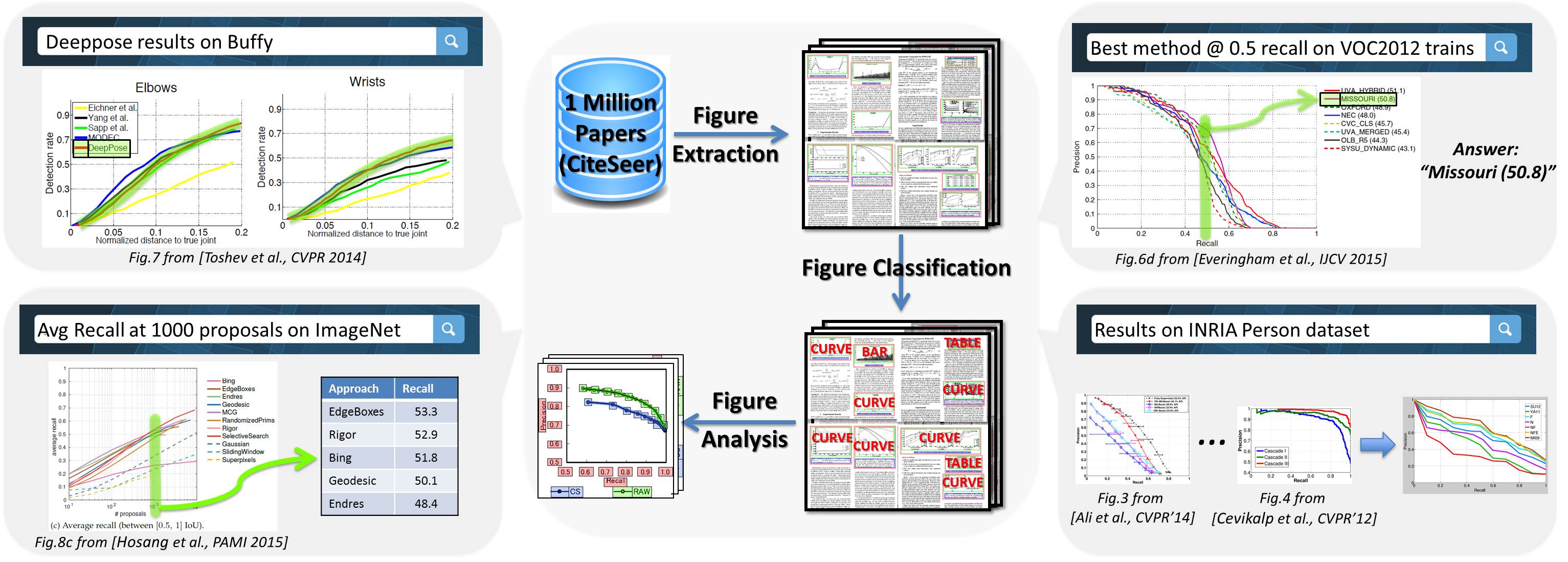
FigureSeer is an end-to-end framework for parsing result-figures, that enables powerful search and retrieval of results in research papers.
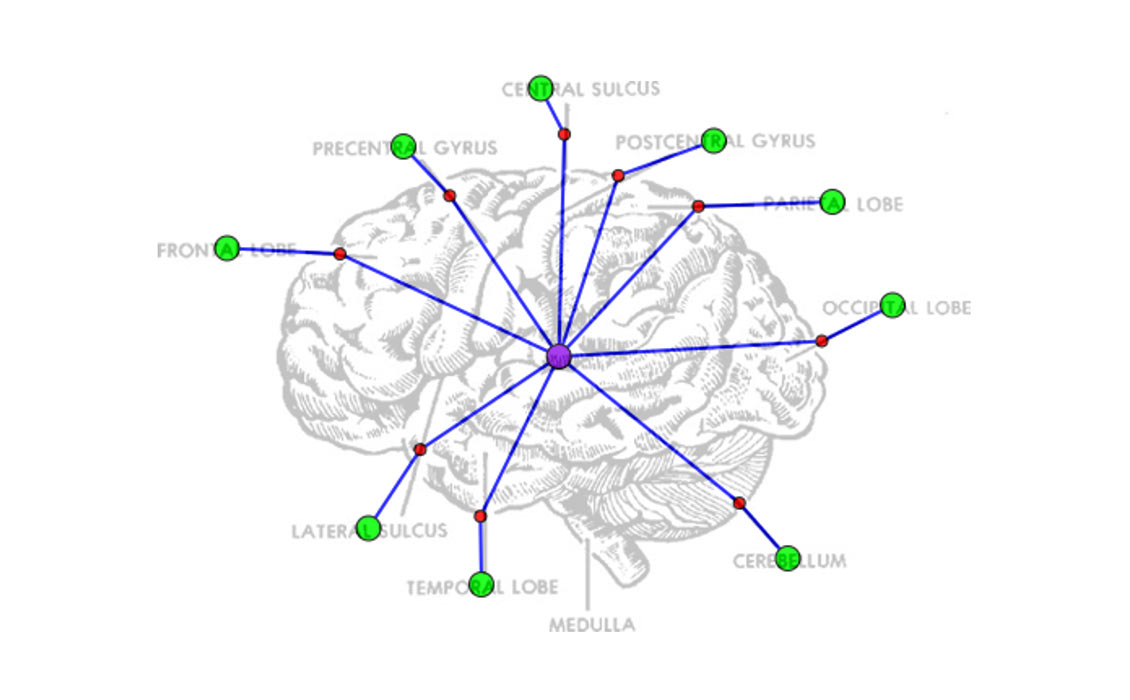
This project aims to parse diagrams and answer the corresponding questions.

A task-oriented recognition approach, where the idea is to find the suitable set of features for each high-level task such that the computation cost is minimized.

Understanding the physics of a scene and the dynamics of objects in images.
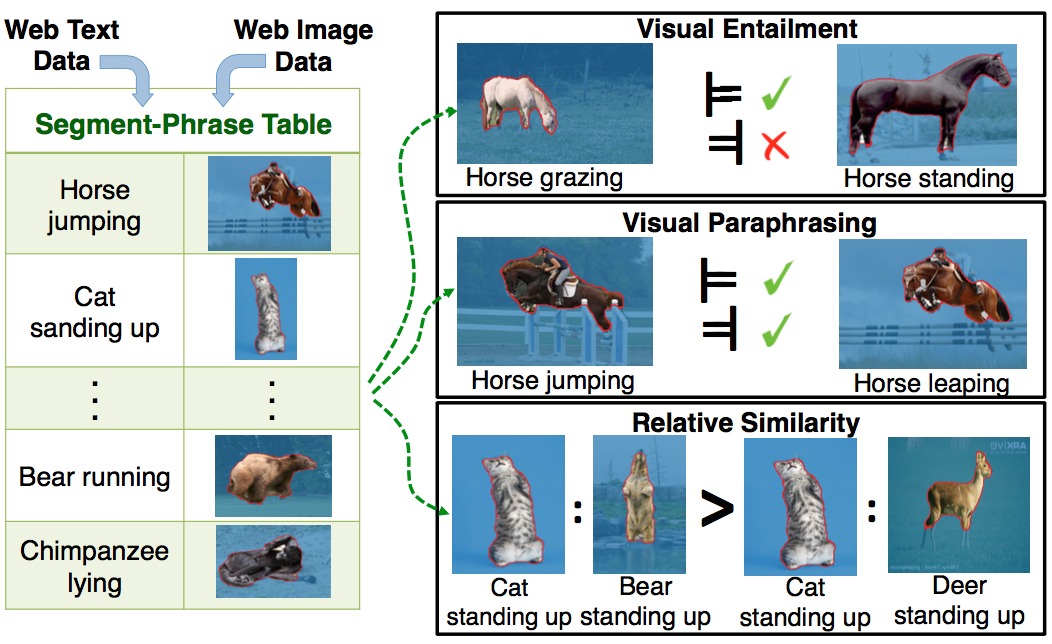
Segment-phrase table is a large collection of bijective associations between textual phrases and their corresponding segmentations.
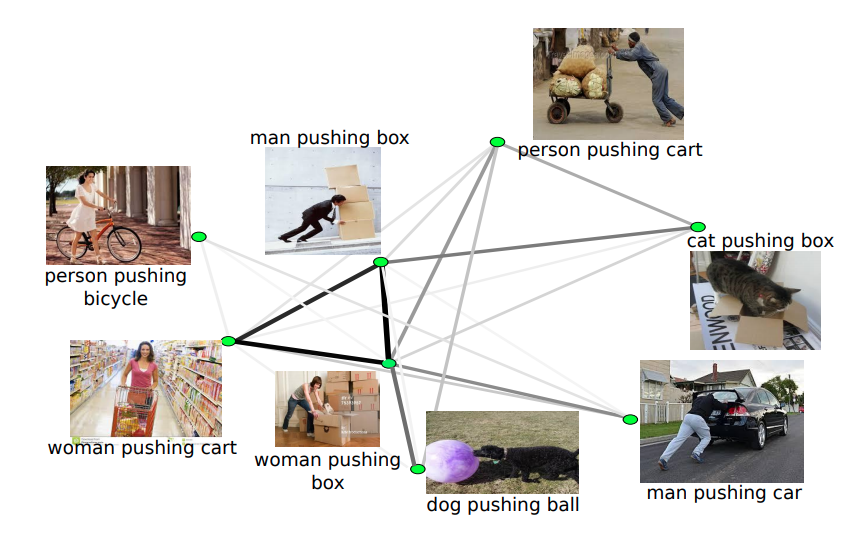
VisKE is a VISual Knowledge Extraction and question answering system built using the idea of scalable visual verification of relation phrases.

LEVAN is a fully-automated visual concept learning program that automatically learns everything there is to know about any visual concept.

AI2-THOR is an open-source, interactive platform for embodied AI research. It allows artificial agents to physically interact with simulated objects and scenes. RoboTHOR extends AI2-THOR to include a series of simulated scenes with real-world counterparts.